How to calculate the cubic meter of the edged board. How to calculate the cube of the unedged board?

For those who work a lot with wooden products, you need to know how to calculate the cabin cube. This knowledge is simply indispensable when calculating the cost of work.
Everything has their own units of measure. Coal is measured in tons, oil - in barrels, population - in thousands of people. That is, some value is taken as the basis, the most fully describes the measured object. It may be weight, quantity or volume. When working with the mass measurement tree, the mass is ineffective, since the density of wood of different rocks differs from each other. In addition, the same board will weigh in different ways, depending on the humidity of the ambient air and the board itself. Therefore, lumber is more convenient to measure in volume. How everyone remembers the School Course of Mathematics, the calculation of it is simple. It is necessary to multiply each other length, width and height. In order to correctly make calculations, it is important to remember that all parameters should be measured in some values. Nothing will happen if you start multiplied millimeters for decimeters. The usual and most convenient unit of measuring linear dimensions is the meter. Accordingly, multiplying the meter on the meter and once again on the meter, we get m³, or cubic meter. In the surprise - cubic meter. And the name of the cubature often applies to wooden products.
Board cube is calculated using special formulas
The cubic meters are measured and a tree growing in the forest, and a bar, and individual logs. Let's look at how to calculate the cabin of the boards.
Lumber cubature
Boards are different. They may differ in length, width or thickness, edged or unedged. But in most cases, these sizes comply with certain standards. If this were not, the calculation of the cube would turn into a very painstaking and long process. Each board would have to wash in all directions. But standardization exists in the woodworking industry. And for all standard sizes There are already calculated lumber volumes and are reduced to the table. They are also called the cabin boards. It is enough to open it on the page with the desired length and the width values \u200b\u200band the thickness of the board determine its volume.

Lumber cube is calculated only by large volumes.
But not everyone has such tables at hand. What to do in this case? As a rule, the boards are not purchased one. Calculate the cube of the edged material can be in the following order. The length and thickness of the board are measured. These sizes are basic, as they must comply with the requirements that are presented to the sawn timber in each particular case. For example, for the crate required a board, 25 mm thick, and for draft floors - 50 mm. Then the width of the material is mixed. W. edged board It's simple because it is cut to a single width. After that, the calculator is taken, all values \u200b\u200b(in one dimension) are multiplied with each other. Thus, the volume of the board with a length of 6 m, a thickness of 50 mm and a width of 15 cm will be:
6 * 0,050 * 0.15 \u003d 0.045 m³
Multiplying this number on the number of boards, it is easy to determine the total volume of wood.
Unedged boards
The case is somewhat more complicated. There is no single width here not only between different boards, but also in each board separately. After all, the tree is uneven in its thickness, it has a larger diameter below than from above. And because one edge of the board is always wider than the other. And this width does not relate to any standards. How to calculate the volume of wood in this case? There are several ways. According to one of them, the width of each board is measured in the middle of its length. This width is called average. This method is acceptable in the case of a small party, but on an industrial scale it will very much delay the work. So that this does not happen, the cabbage of the Unedged Board was developed at one time. The volume values \u200b\u200bin it are obtained empirically, that is, by numerous measurements, and are averaged for each width. The volume calculated in this way is approximate, but deviations from the true value are insignificant.

Unedged board in the cube may differ from the maximum prepared wood to use
Some wood processing enterprises use a stack measurement method. It requires a preliminary sorting of the material so that there are boards in each stack approximately coinciding in width. The length of the board is measured, the average width and height of the entire stack. Multiple values \u200b\u200bmust be additionally multiplied by the fill factor. Its average is 0.67. As you can make sure, with this method, the element of approximacy is also present.
Calculate the cube of the Unedged Board with high accuracy with the weighing. To do this, it is necessary to pre-measure the moisture of wood, as well as know the exact density of the concrete tree. And given the fact that the unedged material is one of the cheapest views of the sawn timber and is used in the least responsible places, such complex calculations are unlikely to meet themselves. In addition, the resulting result of the slight will differ from the cabinetter calculated by the help.
It makes no sense to produce the same calculations several times if the initial data does not change. A log-rounded diameter of 20 cm and 6 meters long will always have the same volume, despite the one who is counting in which city. Only the formula V \u003d πr²l gives the correct answer. Therefore, the volume of one OCB will always be v \u003d 3.14 × (0.1) ² × 6 \u003d 0.1884 m³. In practice, to eliminate the moment of standard computing, cabbage applies. Such useful and informative tables are created for various types of lumber. They help save time and learn the cube of forest-rounding, boards, bruises, timber.
The name of this construction reference book is due to the fact that the volume as a physical value is measured in cubic meters (or cubic meters). For a simpler seizure, the "cube" say, respectively, the table was called "Cubature". This is an ordered matrix into which data is entered on the volume of one product for various initial parameters. The base column holds the sections, and the row is the length (mold) of the material. The user is enough to find the number located in the cell on their intersection.
Consider a specific example - a cube of a round forest. It was approved in 1975, it is called GOST 2708-75, the main parameters - diameter (in cm) and length (in meters). We are very easy to use the table: for example, it is necessary to determine the V single log, having Ø20 cm with a length of 5 m. At the intersection of the corresponding row and column we find the number 0.19 m³. A similar cube for rounding exists according to another standard - ISO 4480-83. References are very detailed in increments of 0.1 m, as well as more general, where the length is taken after 0.5 m.
Small secrets
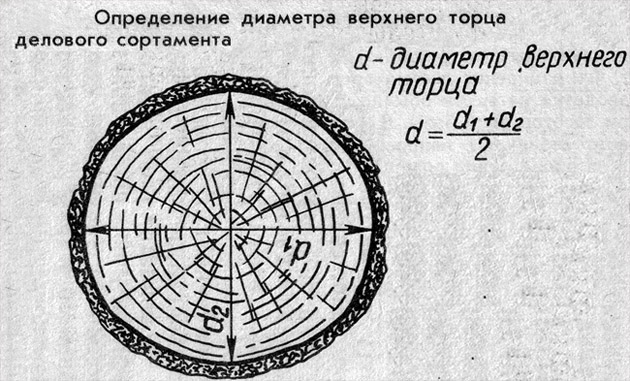
The use of Cubaturenik does not represent any difficulty, but the main nuance is the correct data. Round forest is not a cylinder, but a truncated cone, from which the bottom and the upper arm are different. One of them can be 26 cm, and the other - 18. The table involves an unambiguous answer for a specific section.
Various sources are proposed to come in two ways: carry out the calculation of the average value and take the amount from the directory for it or as the main section to take the size of the upper heap. But if the tables were compiled according to certain standards, then it is necessary to use them according to related instructions. For cube, GOST 2708-75, the diameter of the top sleeve was taken. Why is the moment of source data so important? Because with a length of 5 meters for Ø18 cm we obtain 0.156 m³, and for Ø26 cm - 0.32 m³, which is actually 2 times more.
Another nuance is the right cabbage. If the complex formulas for truncated cones were used in the GOST 2708-75 table, calculations were performed, and the results were rounded to thousandths, then modern companies that make up their own cubeats, allow themselves to "liberty". For example, instead of 0.156 m³ already costs the number 0.16 m³. Often, frankly erroneous cabins are placed on the Internet on the Internet, in which the volume of the log 5 meters long at Ø18 cm is not 0.156 m³, and 0.165 m³. If an enterprise uses such reference books, implementing round forest consumers, then it makes a profit, actually deceiving customers. After all, the difference on 1 product is essential: 0,165-0,156 \u003d 0.009 or almost 0.01 m³.
The main problem of forest-rounding is a different cross section. Solve issues with calculations, sellers are offered in such ways:
- calculating the volume of each unit and summation of the obtained values;
- storage method;
- finding the average diameter;
- a method based on wood density.
1. Immediately need to say that the correct results give the first of these options. Only the calculation of the volume of each log and the subsequent addition of numbers ensures that the buyer will pay for the forest that he will receive from the company. If the length is the same, it is sufficient to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe sections of all trunks, fold them, and then multiply the length (in meters).
2. Warehousing method.
It is assumed that the steady rounder occupies part of the space having the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped. In this case, the total volume is found multiplying the length, widths and height of the figure. Considering that there are emptiness between the folded trunks, 20% will take away from the cubature.
Minus - adoption as an indisputable fact that the tree takes 80% of the total space. After all, it may well happen that the bars are folded inactively, thereby the percentage of emptiness is much more.

3. A method based on density.
In this case, you need to know the mass of the forest and the density of the wood. The cubature is easily divided by the first number to the second. But the result will be very inaccurate, since the tree of one species has a different density. The indicator depends on the degree of maturity and humidity.
4. Averaged method.
If the trunks of the harvested trees on appearance Almost the same, then you choose any 3 of them. Measure diameters, and then find the average value. Next, in the cube, the parameter for 1 product is determined and multiplied by the desired amount. Let the results showed: 25, 27, 26 cm, then Ø26 cm is considered to be average, since (25 + 26 + 27) / 3 \u003d 26 cm.
Considering the disadvantages of the considered methods, the only right way Calculation of the cube can be considered the foundation of each log using the cabinet of GOST 2708-75 or ISO 4480-83 and the summation of the data obtained.
| Articles |
In construction companies and markets, the number of sawn timber measuring in cubic meters (cubes). For someone who is just starting construction, it sometimes causes problems, and some sellers usefully use it.
In fact, the translation of the board or bar from pieces to Cuba and on the contrary is not completely difficult. To do this, it is necessary to determine the volume of one board, given its width, thickness and length.
Determination of the volume of one board
Take as an example the most popular board 50x150, i.e. 5 cm thick board, 15 cm wide. The standard length of the non-stroke board is 6 m (6000 mm). To get a volume in cubic meters, you need to multiply all the dimensions of the boards, expressed in meters, in this case:
0.05 x 0.15 x 6.0 \u003d 0.045
Thus, the volume of one board is equal to 0.045 cubic meters.
Determination of the volume of one bar
The bar is the same board, only fat. The most popular ram 150x150, i.e. thickness and height of 15 cm, standard length - 6 meters. Transfer all sizes to meters, multiply and get 0.135 cubic meters:
0.15 x 0.15 x 6.0 \u003d 0.135
How many boards in one cuba
It would seem here everything is simple. We divide 1 cube to the volume of one board and get the number of boards. For example, for our board 50x150: 1 / 0.045 \u003d 22,22 ...
And for the bar 150x150: 1 / 0,135 \u003d 7.40740 ...
Everything would be fine, but in one Cuba, not a whole number of boards and bars.
Not so simple
Here then we catch the semen forest sellers. One Cube Board - Please - 22 pieces, one cube of timber - Get 7 brusons. For example, for a small house 6x6 need 52 timber - if you consider 52/7 \u003d 7.43 cubes, then you are deceived already on 3 bar.
How to consider it right
We consider total volume:
0.15 x 0.15 x 6.0 x 52 \u003d 7, 02 cubic meters.
Here for these 7.02 cube you must pay, having received exactly 52 bar, and the volume in the cubic meters, and the number of timber must be specified in the invoice.
Other tricks of lumber
In practice, there is the concept of "calibrated" and "unqualted" lumber. They have different permissible deviations from the specified sizes, but also stand in different ways. You must define in advance what tolerances are important and which is not. If you use a 100x150 ram for connecting the sip panels, then the calibrated sawn timber is simply necessary, there will not even help electrulacks, because Unqualted material usually has smaller sizes.
Another feature is a length greater than 6 meters. Usually the average size of the board or bar is not 6 meters, but 6.05. This is due to the fact that the ends are not processed during the cutting process, can be dirty or go at different angles. Clear sellers sometimes (rather rarely) are trying to take into account this in the calculation of cubic meters - but this is a pure sell.
Preparing for construction frame house, the construction of the roof and assembly of the crown of the church, the developer has to be engaged in the purchase of a bar.
This material is used to make various wooden structures, so its sorting has tens of positions. To exclude errors, you need to determine as accurately as possible how many bar in the cubic meter.
The "mathematical model" of this operation is simple. To calculate the volume of any rectangular item, its length is multiplied by width and height. However, in practice, when buying a large number of timber of different lengths and sections, you can get confused and overpay a considerable amount.
In this article we will talk about important nuances of counting the volume of the sawmill and we will give comfortable in the use of the "Cheat Sheets" table to transfer the brown meters in Cuba.
On the forest warehouse be attentive!
Given the high cost of the edged bar, it is necessary to refer to its purchase. Sellers tend to use the price per 1 m3. Customers when calculating the lines of the roof, the wall frame, the beams of overlapping and the floor receives the route meters. Additional confusion make production standards of lengths that are in the range from 3 to 6 meters (step 0.5 meters).
Eliminate everything "on the shelves" in this matter is not difficult. Suppose that you need a timing of 100x50 mm with a sequence of 100x50 mm, and its total length is 100 rose meters (p / m). To count the volume of edged wood, the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bmillimeters is translated into square meters And then multiply them by length: 0.1x0.05x100 \u003d 0.50 m3. We will receive the price of this number of timber, multiplying its volume on the cost of one cubic meter.
And here is another no less important question: how to control the number of a callman who releases you the seller? Here you need to take into account not only the cross section, but also the length of the material.
Suppose that we need a timing of 4 meters long (total length 100 p / m). In this case, the volume of one thing will be equal: 0.1x0.05x4 \u003d 0.02 m3. Dividing the purchased amount of material (0.5 m3) on the volume of one bar (0.02 m3) we will get exactly 25 pieces.
In practice, round numbers are rare, so the required amount of timber is most often obtained by fractional. We will not give the seller to the part of the sawn timber, which remains after the comma. It is better to pay it to the whole number of BRUSEV.
Consider an example. Brous 63 meters are bought (section 100x180 mm, length 6 meters). We consider the volume of purchases: 63x0.1x0.18 \u003d 1,134 m3. We divide it on the volume of one bar (0.1x0.18x6 m / n \u003d 0.108 m3). We get 1,134 / 0.108 \u003d 10.5 pieces. The seller will not cut us half a bar. Therefore, when calculating, it is necessary to supplement it to a whole amount and pick up 11 bars.
With a profiled timber, the cross section of which has a complex form, come in the same way as with the usual one. To determine the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthis material, its total height (the distance from the bottom face with the groove to the top of the spike) is multiplied by the width.
Considering the amount of timber in 1m3 in stock, take the roulette and measure the actual cross section of the purchased material. It may turn out that instead of the 100x200 or 150x150 mm promised by the seller 100x200 or 150x150 mm, a thinner material was delivered. Even 1 centimeter reduction of the transverse size of the sawmill turns into substantial losses for the buyer.
Another important nuance is the technological deviation of the length of the bar. It can reach 5-7 centimeters, since the ends of the logs are not cut in the processing process. Remember that the seller does not have the right to plus these extra centimeters to the total length.
Tables for quick counting volume of timber
Read on the calculator how many pieces of a bar in Cuba is not always convenient, especially when buying a big party. Seller data can be easily monitored by finished tables. Here, for standard sizes of the sawmaker, information is provided in volume of 1 timber and the number of pieces in 1m3.

Table for counting edged timber 6 meters long
| Dimensions (mm) | Volume 1 piece (m3) | Pieces per 1 m3 |
| 100x100x6000. | 0,06 | 16 |
| 100x150x6000. | 0,09 | 11 |
| 100x180x6000. | 0,108 | 9 |
| 100x200x6000 | 0,12 | 8 |
| 150x150x6000. | 0,135 | 7 |
| 150x180x6000. | 0,162 | 6 |
| 150x200x6000 | 0,18 | 5,5 |
| 180x180x6000. | 0,1944 | 5 |
| 180x200x6000. | 0,216 | 4,5 |
| 200x200x6000. | 0,24 | 4 |
| 250x200x6000. | 0,3 | 3 |
This table can also be used when purchasing a 3-meter bar. For this, the volume of 1 thing needs to be reduced by half, and the amount of material in one Cuba is multiplied by 2.
Recall that the timber with a thickness and width of 100 mm and more is considered a timber by definition. Therefore, we intentionally did not include in the table the size of wooden blanks of a smaller cross section to comply with formal accuracy.
Let's look at the data on the volume and number of boards of running size in a separate table:
| Dimensions (mm) | Volume 1 piece (m3) | Pieces per 1 m3 |
| 25x100x6000 | 0,015 | 66,6 |
| 25x150x6000. | 0,0225 | 44,4 |
| 25x200x6000 | 0,03 | 33,3 |
| 40x100x6000. | 0,024 | 41,6 |
| 40x150x6000. | 0,036 | 27,7 |
| 40x200x6000 | 0,048 | 20,8 |
| 50x50x6000 | 0,015 | 66,6 |
| 50x100x6000. | 0,03 | 33,3 |
| 50x150x6000 | 0,045 | 22,2 |
| 50x200x6000 | 0,06 | 16,6 |
| 50x250x6000. | 0,075 | 13,3 |
To count the volume and quantity of 4 meter bar, you can use the following table-crib:
| Dimensions (mm) | Volume 1 piece (m3) | Pieces per 1 m3 |
| 100x100x4000 | 0,04 | 25 |
| 100x150x4000 | 0,06 | 16,66 |
| 100x180x4000. | 0,072 | 13,88 |
| 100x200x4000 | 0,08 | 12,5 |
| 150x150x4000 | 0,09 | 11,11 |
| 150x180x4000. | 0,108 | 9,26 |
| 150x200x4000 | 0,12 | 8,33 |
| 180x180x4000 | 0,13 | 7,69 |
| 180x200x4000 | 0,144 | 6,94 |
| 200x200x4000 | 0,16 | 6,25 |
| 250x200x4000 | 0,2 | 5 |
As can be seen from the table, almost the entire range of BRUSEV is obtained by fractional. Therefore, for economical purchase, you should take advantage of our advice on the seller to the whole number of timber.
How to make it practically? Let us give an example. Suppose that we bought one cubic meter of a 4-meter bar with a cross section of 100x180 mm (the table turns out 13.88 pieces). The price of 1m3 is 6500 rubles. Up to 14 pieces of BRUSEV, we need to pay 14-13.88 \u003d 0.12. The volume of this "piece" is (0.12 x 4 meters \u003d 0.48 m) x 0.1x0.18 m \u003d 0.00864 m3. I multiply it on the price of 1 m3 and we get 0.00864 m3 x 6500 rubles. \u003d 56.15 rubles.
Remember that the purchased volume of bars should include a supply (loss during cutting during operation). Therefore, the result obtained in the process of the theoretical counting of the rafting system of the roof or other wooden structure must be multiplied by the coefficient of 1.3. After this adjustment, you can start calculations with the seller.
In addition to determining the volume and price of the purchased material, you need to know the weight of 1m3 of the bar, to order the transport of the appropriate carrying capacity.
The weight of the cubic meter of the bar depends on the wood breed and from its humidity. The approximate mass of 1m3 dry pine is 510 kg (raw - 890 kg).
The average weight of one cube of brucks from dry fir is equal to 450 kg (raw - 790 kg).
The weight of the dried oak wood is in the range from 700 to 800 kg / m3, and wet (freshly fresh) - from 980 to 1030 kg / m3.
The dry bar of larch weighs 650 kg / m3. Fresh material of this breed of wood weighs 840 kg / m3.
Before buying a floorboard, you need to calculate how much the cubes of sawn timber for the device of a particular design. In this case, the accurate calculation can be done using a conventional calculator, knowing the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the thickness of the board. Such skills will be useful to you not only in order to calculate the volume of sawn timber for flooring, but also in case you decide to build a house, because wood products are used for the construction of various designs.
Since the price of all sawn timber is charged for the cube, it is important to be able to calculate the need for this unit of measurement. This is so calculated not only by the number of boards, but also other lumber, such as timber, rails, etc. The thing is that products with the same cross section may differ long. Therefore, after determining the volume, it can be understood how many Halves will be in one Cuba.
It is important to know: when buying a chalkboard from a valuable wood product, products are sold individually. The thing is that the price of such coatings is too large, and when calculating in the cubes there is a small error.
When calculating it is better to use the usual calculator. So you can get a more accurate result and take into account all the nuances of the future design of the house. Although if you need to know how many cup cubes, for example, a 50 mm thick, you will need for a floor device, you can use and online calculator. Such a simple calculation can be done correctly. Nevertheless, it is always useful to be able to count the number of sawn timber.

During the construction of the house or the flooring of the floor, the calculation is carried out in the same order:
- First you need to calculate the total volume of lumber in the cubes. Knowing wood moisture, you can decide on the weight of the entire material. It will help to decide which product delivery method to choose.
Tip: When ordering the carrier, it is better to specify the overestimated weight (10-15% more). So you will have no problems with the cargo, because the moisture declared by the manufacturer may be slightly larger or less.