As the Atlantic Ocean appeared. Atlantic Ocean: flows in the water area and their influence on the climate. Maximum and average ocean depth
The Atlantic Ocean is considered one of the largest and voluminous largest, namely the second size after the Pacific Ocean. This ocean, the most studied and mastered, if compared with other waters. Its located is as follows: from the east is framed by the shores of North and South America, and in the west of its borders ends Europe and Africa. In the south, he goes to the southern ocean. And from the northern side borders with Greenland. The ocean is characterized by the fact that it has very few islands, and its bottom relief is all twisted and has a complex structure. The line of the coast is broken.
Characteristics of the Atlantic Ocean
If we talk about the ocean area, it takes 91.66 million square meters. km. It can be said that part of its territory is not the ocean itself, but the existing seas, bays. Ocean volume 329.66 million square meters. km, and its average depth of 3736 m. Where the Puerto Rico gutter is located, it is considered the biggest depth of the ocean, which is 8742 m. The flows allocate two - North and South.

Atlantic Ocean on the North side
The border of the ocean from the north in some places is marked by ridges located under water. In this hemisphere, the Atlantic is framed by the rugged shore line. Its small northern part is connected to the Northern Arctic Ocean with several narrow straits. The devisians of the Strait are located in the northeast and connects the ocean with the sea of \u200b\u200bBuffin, which is also considered to belong to the Arctic Ocean. Closer to the center there is a Danish strait less wide than the devisians. Between Norway and Iceland closer to the northeast is the Norwegian Sea.
In the southwest of the northern flow of the ocean, there are a Mexican bay, which is connected by the Floridian strait. And also the Caribbean Sea. Here you can mark a lot of bays, such as barnegate, Delaware, Hudsons Bay and others. It is in the northern side of the ocean that you can see the largest and large islands that are famous for their fame. This is Puerto Rico, world-famous Cuba and Haiti, also British Islands and Newfoundland. Closer to the east you can find small clubs of the islands. This is the Canary Islands, Azores and Green Cape. Closer to the West - Bahamas, small antilles.

South of the Atlantic Ocean
Some of the geographers believe that the southern part is all the space to the Antarctic. Someone determines the border at Cape Mountain and Cape of the Good Hope of two continents. The shore in the south of the Atlantic Ocean is not so cut as in the north, and there is no seas. There is one major bay near Africa - Guinean. The most distant point in the south is a fiery land that is framed by small islands in large quantities. Also, it is also impossible to meet big islands, but there are separate islands as about. Ascension, St. Helena, Trustee-Kunya. At the most extreme south, you can meet the Southern Islands, Buvet, Falkland and others.
As for the flow in the south of the ocean, here all systems are coming counterclockwise. Near the East of Brazil, the southern trade house is branched. One branch goes to the north, proceeds near the north shores of South America, filling the Caribbean. And the second is considered southern, very warm, moving near Brazil and soon connects with the Antarctic current, then it is sent to the eastern side. Partially separated and turns into a Bengelege course, which is distinguished by its cold waters.
Atlantic Ocean Attractions
There is a special underwater cave in the Belize Barrier Reef. It was called a blue hole. It is very deep, and inside it is still located a number of caves that are connected by the tunnels. The depth of the cave reaches 120 m and is considered unique in its kind.

There is no man who would not know about the Bermuda triangle. But it is located in the Atlantic Ocean and excites the imagination of many superstitious travelers. Bermuda mounted with their mysteriousness, but at the same time frighten the unknown.

It is in the Atlantic that you can see an unusual sea that has no shores. And all because it is located in the middle of the water space, and its borders cannot be framed by land, only the currents show the boundaries of this sea. This is the only world world that has such unique data and is called Sargasso Sea.
If you like this material, share it with your friends on social networks. Thank you!
It ranks second in the world after the Pacific Ocean. Its square takes about 20% of the entire surface of the Earth. The water of the Atlantic Ocean is the most salty taste. According to its form, which was purchased after the smoke group, Pangea, the ocean resembles the letter S.
Features of the geographical position of the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic is the most mastered ocean of the world. In the east, he borders on the coasts of South and North America. In the north, the Atlantic Ocean is washes cold Greenland, and in the south merged with the Southern Ocean. In the west of its borders outlined by African and European shores.
The total area of \u200b\u200bthe Atlantic is about 91.66 million square meters. km. The geographical position of the Atlantic Ocean causes a wide amplitude of its temperatures. In the south and north, the water temperature is 0 ° C, and at the equator - 26-28 ° C. The average depth of the Atlantic Ocean is 3736 m, and the deepest depression is Puerto Rico's chute - 8742 m.
Among the flows, scientists conventionally denote two cyphans. This is the northern, in which the flows carry out movement clockwise, as well as the South, where they flow counterclockwise. These circulation are separated by equatorial interpassate anti-countercord. In high school in the geography lessons, the geographical position of the Atlantic Ocean (Grade 7) is studied in detail.

Many believe that the oceans are almost eternal and will exist until the end of history. But it is not so. For example, from the ancient Ocean of Tettis, once located between the continents of Laurelasia and Gondwayn, now there are only Mediterranean, Black, Caspian Sea and a small Persian bay. The same fate can comprehend the Atlantic Ocean. The geographical position of the continents here plays a far from the last role.

The Ocean Tethis disappeared from the face of the Earth when Africa and India became rapidly approaching the Eurasian continent. Researchers believe that the Atlantic Ocean is now rapidly. Scientists have discovered that intensive processes of subducts are undergoing in its day - the immersion of one sections of the earth's crust under the other.
Walking through the ocean
In 1988, the Frenchman Remy Bric reinforced the Atlantic Ocean on foot. The geographical position of the desperate traveler was monitored using special equipment. To the feet, he tied five-meter pontoons made of fiberglass. Around the brick pulled the raft on which the technique for desalination of water and fishing rods was. The traveler went from the Canary Islands and planned to get to Guadeloupe. Brick was very stupid, and he began hallucinations, so it was picked up near Trinidad with the help of trawler. Despite this, the Administration of the Guinness Records of Records The Khrubromograd record.
"Konsky latitude" of the Atlantic
Sargassovo Sea is one of the most amazing, which has the Atlantic Ocean. The geographical location of the sea is such that the zone of constantly increased atmospheric pressure is above it. Therefore, the calm is dominated in Sargasso Sea all the time. During the Sailing Fleet, this place was disastrous for many ships. Often, Sargassa is called "horse latitudes". This is due to the fact that before the courts from Europe in America often transported domestic animals, most often horses. Horses often died, and the corpses were simply thrown overboard in the Sargasso Sea.

Sea without borders leaving horror
For antiquity navigators, this sea inspired a real fear. On his surface, which the tenacious algae was abandoned, a lot of ships stopped. Travelers called it differently: the sea of \u200b\u200bspirits, the sea, which cannot be twisted, the sea of \u200b\u200bfragments. Scientists still continue to make amazing discoveries, revealing the secrets of Sargassov Sea.
But for the first time he witnessed Christopher Columbus. In 1492 he sailed on the ship, trying to find a short way to India. The crew was looking forwarded when the land strip appears on the horizon. But it turned out that the sailors were taken for the mainland a huge accumulation of algae on the surface of the terrible sea. With great difficulty, Columbus managed to overcome a huge water meadow.
Scary Bermuda Triangle
Bermuda Triangle is another full mystical riddles area that has the Atlantic Ocean. The geographical position of this zone is such that in its form it is conventionally indicated as a triangle. It is located between the Bermuda Islands, the coast of Florida and Island in Puerto Rico. Here, during the entire history, ships and aircraft mysteriously. The term "Bermuda Triangle" appeared only after the release of Vincent Gaddis, which was called the Bermuda Triangle - the Devil's Lair.
The reason for the permanent formation of water films
From the west of the sides, this mysterious place is almost completely streamlined by Golf Stream. In these places, the temperature usually does not exceed 10 degrees. Due to the collision of temperatures, a fog is often formed here, affecting the imagination of too impressionable sailors. In addition, the golfustrim speed reaches about 10 km / h. For comparison: the speed of modern vessels ranges from 13 to 30 km / h. Therefore, it is not surprising that many small ships in the past simply knocked down from the course or they drowned in the ocean puchin. In addition to Golf Stream, in the area Bermuda triangle Spontaneous currents arise, to guess the direction of which is impossible. As a result, terrible waterways are formed here.
Bermuda triangle is located in the Passyat zone. Almost all the time blowing the storm winds. According to statistics, on average per year accounts for 80 days of a storm, which means that every fourth day in the area of \u200b\u200bthe Bermuda triangle the weather is disgusting.

Why did the ships died?
However, not only powerful winds and the flow of the Bermuda zone were the cause of the death of numerous ships. The ocean here is able to generate infrasound signals, which cause a strongest panic from any living organism, whether it is a person or waterfowl. Due to psychological pressure, people were able to even be thrown overboard.
In the process of generating these waves, storm winds play a considerable role, fighting about high waves. When air strikes arise about the crest of the waves, a low-frequency wave is formed, immediately rushing forward. She catches a floating ship and finds himself in his cabins.
When the infrared signal enters the closed space of the ship cabin, its impact on people is almost unpredictable. Many begin hallucinations, and they begin to see their most terrible nightmares. Without withstanding psychological pressure, the entire crew can be thrown into the oceanic abyss, and the ship will be found empty.
Modern scientists believe that the cause of mystical phenomena is methane deposits at the bottom of the Bermuda Triangle. They are rich not only the Atlantic Ocean. The geographical position of many places of the World Ocean is such that other zones can be comparable in danger with a Bermuda triangle.

Atlantic Ocean and Modern World
Atlantic is characterized by a huge variety of biological species. Here every year is mined the largest number of fish calculated by millions of tons. In addition, the Atlantic Ocean is one of the busiest sea routes. On the shores of the Atlantic there is a lot of resort zones. Despite the fact that the geographical position of the Atlantic Ocean, it is constantly contaminated by factory waste. In its water is reset the pesticides and fertilizers. Sometimes the tankers crashes towards huge petroleum pollution. Save the Atlantic - the global task of all mankind.
The Atlantic Ocean - the second largest ocean of the land after the Pacific Ocean, located between Greenland and Iceland in northern, Europe and Africa in the East, North and South America in the West and Antarctica in the south.
The area of \u200b\u200b91.6 million km², of which about a quarter comes from the incontinental seas. The area of \u200b\u200bthe coastal seas is small and does not exceed 1% of the total area of \u200b\u200bthe water area. The volume of water is 329.7 million km³, which is equal to 25% of the volume of the world's ocean. The average depth is 3736 m, the largest - 8742 m (Puerto Rico's fruit). The average annual salt water of the ocean is about 35. The Atlantic Ocean has a strongly rugged coastline with a pronounced division into regional water areas: seas and bays.
The name happened on behalf of Titan Atlas (Atlanta) in Greek mythology.
Characteristics:
- Area - 91.66 million km²
- Volume - 329.66 million km³
- The greatest depth - 8742 m
- Average depth - 3736 m
Etymology
The name of the ocean first occurs in the V century BC. e. In the works of the ancient Greek historian Herodotus, who wrote that "the sea with the poles of Hercules is called Atlantis (Dr.-Greek. ἀἀΛανίςίς - Atlantis)." The name comes from the famous Miph of Atlanta in ancient Greece about Atlanta, Titan, holding the heavenly arch in the extreme western point of the Mediterranean. The Roman Scientist Pole Senior in the first century is used by the modern name Oceanus Atlanticus (Lat. Oceanus Atlanticus) - "Atlantic Ocean". At different times, individual parts of the ocean called the West Ocean, the North Sea, the outside sea. Since the middle of the XVII century, the Atlantic Ocean has become the only name relating to the whole water area.
Physico-geographical characteristics
General
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest. Its area is 91.66 million km², water volume - 329.66 million km³. It extends from subarctic latitudes to the Antarctica itself. The border with the Indian Ocean passes through the Meridian of Cape Needle (20 ° B.D.) to the coast of Antarctica (the Land of the Queen mod). The border with the quiet ocean is carried out from Cape Horn according to Meridian 68 ° 04 'z. either by the shortest distance from South America to the Antarctic Peninsula through the Strait of Drake, from the island of Oste to Cape Sternek. The border with the Arctic Ocean runs along the eastern entrance of the Hudson Scholiva, then through the devisians, and along the coast of Greenland Island to Cape Bruster, through the Danish Strait to Cape Radinupure on the island of Iceland, according to His coast before Cape Herpir, then to the Faroe Islands, further to Shetland Islands and 61 ° north latitude to the coast of the Scandinavian Peninsula. Sometimes the southern part of the ocean, with the northern border from 35 ° YU. sh. (on the basis of circulation of water and atmosphere) to 60 ° sh. (According to the nature of the Relief of the bottom), refer to the Southern Ocean, which is not officially allocated.
Sea and bay
The area of \u200b\u200bthe seas, the bays and the straits of the Atlantic Ocean is 14.69 million km² (16% of the total area of \u200b\u200bthe ocean), the volume of 29.47 million km³ (8.9%). Sea and main bays (clockwise): Irish Sea, Bristol Bay, North Sea, Baltic Sea (Batnic Bath, Finnish Bay, Riga Bay), Biscay Bay, Mediterranean Sea (Sea Alboran, Balearia Sea, Liguria Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, Adriatic Sea, Ionian Sea, Aegean Sea), Marmara Sea, Black Sea, Azov Sea, Guinean Bay, Sea Risser-Larsna, Sea Lazarev, Sea Weddell, Sea Skee (the last four sometimes belong to the South Ocean), Caribbean Sea, Mexican Bay , Sargasso Sea, Maine Bay, Saint Lawrence Bay, Labrador Sea.
Islands
The largest islands and archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean: British Islands (United Kingdom, Ireland, Hebrid Islands, Orkney Islands, Shetland Islands), Large Antilles (Cuba, Haiti, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Hoisitud), Newfoundland, Iceland, Archipelago Fire Earth (Fire Earth, Oste, Navarino), Maramery, Sicily, Sardinia, Small Antilles (Trinidad, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Curaçao, Barbados, Grenada, Saint Vincent, Tobago), Falkland (Malvinsky) Islands (East Falkland (Soledad), Western Falkland (Grand-Malvina)), Bahamas (Andros, Big Inagua, Big Bahamas), Cape Breton, Cyprus, Corsica, Crete, Antiquities, Canary Islands (Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Grand Canaria), Zealand, Prince Eduard, Balearic Islands (Mallorca), South George, Long Island, Moison Archipelago (Saaremaa, Hiyumaa), Green Cape Islands, Evie, Southern Sporads (Rhodes), Gotland, Funen, Cyclades, Azores, Ionian Islands, South Shetland Islands, B Ioko, Bezhagosh Islands, Lesbos, Aland Islands, Faroe Islands, Eland, Lolland, South Orcane Islands, Sao Tome, Madeira Islands, Malta, Principe, Saint Helena, Ascension, Bermuda Islands. 
The history of the formation of the ocean
The Atlantic Ocean was formed in the Mesozoy as a result of the split of the ancient supercontinent of Pangea on the southern mainland of Gondwan and the Northern Lavra. As a result of the multidirectional movement of these continents at the very end of Triass, led to the formation of the first ocean lithosphere of the current North Atlantic. The formed rift zone was a Western continuation of the rift crack of the Ocean Tetis. Atlantic Wpadina at an early stage of its development was formed as the combination of two large ocean pools Ocean Tetis in the east and the Pacific in the West. The further growth of the depression of the Atlantic Ocean will be held by reducing the size of the Pacific Ocean. In early Russian time, Gondwan began to split into Africa and South America and the ocean lithosphere was formed by modern South Atlantic. In the chalk time, laurels broke up, and the branch of North America began from Europe. At the same time, Greenland, shifting to the north, soldered from Scandinavia and Canada. Over the past 40 million years and up to the present time, the disclosure of the Atlantic Ocean basin on a single rift axis, located approximately in the middle of the ocean, continues. Today the movement of tectonic plates continues. In the South Atlantic continues the discrepancy between the African and South American plates at a speed of 2.9-4 cm per year. In the Central Atlantic, the African, South American and North American plates at a rate of 2.6-2.9 cm are diverged per year. In North Atlantic, the spreading of Eurasian and North American plates with a speed of 1.7-2.3 cm per year. North American and South American plates move to the West, African to the Northeast, and Eurasian southeast, forming a compression belt in the Mediterranean area. 
Geological structure and relief
Underwater edge of the mainland
Significant Schelf Square are confined to the northern hemisphere and adjacent to the shores of North America and Europe. At Quaternary times, most of the shelf was subjected to mainland beaming, which formed the relic ice mills. Another element of the relic relief of the shelf is flooded river valleys, found in almost all shelves of the Atlantic Ocean. Relic continental deposits are widespread. At the shores of Africa and South America, the shelf occupies smaller square, but in the southern part of South America, it significantly expands (Patagonian shelf). Sand ridges have been formed with tidal flows that have become the greatest distribution of modern subak-valid form of relief. They are very characteristic of the shelf Northern Sea, in large quantities are found in La Manne, as well as on the shelves of Northern and South America. In equatorial-tropical waters (especially in the Caribbean, in the Bahamas, coral reefs are diverse and widely represented by the coast of South America). 
The mainland slopes in most areas of the Atlantic Ocean are expressed by steep slopes, sometimes having a stepped profile and deeply dissected by underwater canyons. In some areas, mainland slopes are complemented by edge plateau: Blake, São Paulo, Falkland on American underwater outskirts; Bibin and Goban on the underwater edge of Europe. The block structure is the Farrero-Icelandic threshold extending from Iceland to the North Sea. In the same region there is an elevation of a rockey, which is also a submerged part of the underwater part of the European subcontinent.
The continental foot, on most of the stretch, is the accumulation plain lying at a depth of 3-4 km and folded powerful (several kilometers) of the thick bottom precipitation. Three rivers of the Atlantic Ocean are among the top ten in the world - Mississippi (solid stock 500 million tons per year), Amazon (499 million tons) and orange (153 million tons). The total amount of sedimentary material, which is made annually into the Atlantic Ocean Pool, only 22 of its main rivers is more than 1.8 billion tons. In some areas of the mainland foot, large cones of the torment of the torment of the underwater canyons of the Hudson, Amazon, Rhons are most significant among them. (in the Mediterranean), Niger, Congo. Along the North American continental outskirts due to the bottom flow of cold Arctic waters along the mainland foot in the southern direction, gigantic accumulation forms of relief are formed (for example, "sediment ridges" Newfoundland, Blake Bahamas and others).
Transition zone
Transition zones in the Atlantic Ocean are represented by areas: the Caribbean, the Mediterranean and the Sea region of the Bloom or South Sandwich.
The Caribbean region includes: the Caribbean, the deep-sea part of the Gulf of Mexican, island arcs and deep-water gutters. It can distinguish the following island arcs: Cuban, Cayman Siera-Maestra, Jamaica-South Haiti, the external and inner arc of the small antillest islands. In addition, the underwater elevation of Nicaragua, the Range of Beat and Avesta. Cuban arc has a complex structure and has a laramomy age of folding. Its continuation is the Northern Corderar Island Haiti. The folded structure of Cayman-Siera-Maesstra, having myocene age, begins the Maja mountains on the Yucatan Peninsula, then continues in the form of a submarine ridge of Cayman and the South Cuba Siera Maestra ridge. The little-antiller arc includes a number of volcanic formations (including three volcanoes, such as Montan Pele). The composition of the eruptions products: Andesites, basalts, datsites. External arc ridge - limestone. From the south, the Caribbean Sea is born two parallel young ridges: the arc of leeward islands and the Caribbean chain, turning to the east of Trinidad and Tobago. Island arcs and underwater ridges divide the bottom of the Caribbean sea for several kotlovin, which are aligned with powerful thick-to-carbonate bottom sediments. The deepest one is Venezuelan (5420 m). Here there are two deep-sea gutters - Cayman and Puerto Rico (from the greatest depth of the Atlantic Ocean - 8742 m).
The areas of the ridge of the right and southern sandwich islands are Borderland, sites of underwater continental outskirts, fragmented by tectonic movements of the earth's crust. The island arc of the South Sandwich Islands is complicated by a number of volcanoes. From the east, a south-sandwiche deep-water gutter is adjacent to it with a maximum depth of 8228 m. Mountain and hilly relief of the bottom of the sea is associated with the axial zone of one of the branches of the mid-oceanic ridge.
In the Mediterranean Sea, there is a wide propagation of continental terrestrial crust. Subochangeanic earth's crust It is only developed by stains in the deepest basins: Balearic, Tyrrhenian, Central and Cretan. The shelf is essential only within the Adriatic Sea and the Sicilian Mortgage. The mountain folding structure connecting the Ionian Islands, Crete and Islands to the east of the latter, is an island arc, which is limited to the south of Hellensky, which, in turn, from the south, framed by the raising of the East Mediterranean shaft. The bottom of the Mediterranean Sea in the geological section is composed of solenous strata of the Messinsky tier (Upper Miocene). In the Mediterranean Sea is a seismic zone. There are several acting volcanoes (Vesuvius, Etna, Santorin).
Mid-Atlantic Range
The Meridional Mid-Atlantic Range divides the Atlantic Ocean on the Eastern and Western part. It begins off the coast of Iceland called Reykyanenes Range. Its axial structure forms a basalt comb, rift valleys in the relief are poorly pronounced, but the existing volcanoes are known on the flanks. On a latitude of 52-53 ° S.Sh. The mid-oceanic ridge intersect the transverse zones of Gibbs and Reykjanes fault areas. The Mid-Atlantic Range begins behind them with a clearly pronounced rift zone and rift valleys with numerous transverse faults and deep rake. On the latitude of 40 ° C.Sh. The average and oceanic ridge forms Azores volcanic plateau, with numerous supervolored (forming islands) and underwater existing volcanoes. To the south of the Azores Plateau in the rift zone under limestalls with a capacity of 300 m Basalts, and under them a boulder mixture of ultrabasic and main rocks. In this area there are modern stormy volcanic and hydrothermal activities. In the one-digitatorial part, the north-Atlantic ridge is divided into a large number of transverse faults on a number of segments experiencing significant (up to 300 km) lateral displacements relative to each other. The equator with deep-sea faults is associated with a vpadina Romanesh with depths to 7856 m.
The South Atlantic Ridge has a meridional strike. Reftovy valleys are well expressed here, the number of transverse faults is less, so this ridge looks more monolithic compared to the North Atlantic ridge. In the southern and middle parts of the ridge, volcanic Ascension Plateau, Tristan da Cunya islands, Gof, Buvet are distinguished. Plateau is timed to the current and recently operated volcanoes. From Buvea Island, the South Atlantic Ridge turns to the east, envelopes Africa and in the Indian Ocean closes with the West Indian Middle Range.
Ocean bed
The middle-atlantic ridge divides the airfield of the Atlantic Ocean into two almost equal parts. In the western part of the mountain structures: Newfoundland Ridge, Barat Where Ridge, Raising Seara and Rio Grandi share the ocean bed for the basins: Labrador, Newfoundland, North American, Guiangskaya, Brazilian, Argentinean. East of the mid-ocean ridge, the bed is divided by the underwater base of the Canary Islands, raising the islands of the green cape, the Guinean raising and the whale ridge to the basins: Western European, Iberian, North African, Green Cape, Sierra Leone, Guinean, Angolan, Kapskaya. Flat Assual Plains, composed mainly of lime-based biogenic, and terrigenous material are widespread in the basins. For most of the Ocean Lodge Square, precipitation capacity is more than 1 km. Under sedimentary rocks, a layer was detected by volcanic rocks and compacted sedimentary rocks.
In the areas of Kotlovin, removed from the underwater pains of the mainland, the periphery of the mid-ocean ridges are common absession hills. About 600 mountains are located within the Ocean Lodge. A large group of underwater mountains is timed to the Bermuda Plateau (in the North American Both). There are several large underwater valleys, of which the most significant valleys of Heisen and Mori in the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean Lodge, stretching on both sides of the mid-ocean ridge.
Bottom sediments
The deposits of shallow parts of the Atlantic Ocean are presented mostly by terrific and biogenic sediments, and occupy 20% of the area of \u200b\u200bthe ocean bottom. Among deep-water deposits are the most common lime foraminiferous yers (65% of the area of \u200b\u200bthe ocean bottom). In the Mediterranean and Caribbean seas, in the southern zone of the South Atlantic ridge, the spread of pteroid deposits. A deep-sea red clay occupies about 20% of the area of \u200b\u200bthe ocean bottom and is timed to the deepest parts of the oceanic boiling. In the Angolattas, there are radary ils. In the southern part of the Atlantic, siliceous diatoms are presented with an auticon silica content of 62-72%. In the zone of the flow of Western winds, a solid field of diatom zlov is stretched, with the exception of the drill strait. In some, terrigenous aleurites and pelits are significantly developed in the ocean bed of the ocean. Terigenic deposits on abissual depths are characteristic of North Atlantic, Hawaiian, Argentine Kotlovin.
Climate
The variety of climatic conditions on the surface of the Atlantic Ocean is determined by its large meridional length and circulation of air masses under the influence of four major atmospheric centers: the Greenland and Antarctic maxima, Icelandic and Antarctic minima. In addition, two anticyclone are constantly in subtropics: Azores and South Atlantic. They are divided by the equatorial area reduced pressure. Such a distribution of the Baric regions determines the system of dominant winds in the Atlantic. Not only its large meridional length is the greatest effect on the temperature regime of the Atlantic Ocean, but also water exchange with the Northern Arctic Ocean, the seas of Antarctic and the Mediterranean Sea. For surface waters, their gradual cooling is characterized as it removes from the equator to high latitudes, although the presence of powerful currents causes significant deviations from zonal temperature modes. 
On the expanses of the Atlantic are all climatic belts of the planet. For tropical latitudes are characterized by minor seasonal temperature fluctuations (the average indicator is 20 ° C) and abundant precipitation. To the north and south of the tropics there are subtropical belts with more noticeable seasonal (from 10 ° C in winter to 20 ° C in summer) and daily temperature fluctuations; The precipitation here falls mainly in the summer. Frequent phenomenon in the subtropical zone - tropical hurricanes. In these monstrous atmospheric vortices, wind speed reaches several hundred kilometers per hour. The most powerful tropical hurricanes are rampant in the Caribbean: for example, in the Gulf of Mexico and on the Islands of West Indies. West-Indian tropical hurricanes are formed in the western part of the ocean in the region of 10-15 ° S.Sh. And move to the Azores and Ireland. Next to the north and south, the zones of subtropics are followed by the zones of subtropics, where in the coldest month the temperature decreases to 10 ° C, and in winter the cold air masses from the polar areas of low pressure brought abundant precipitation. In moderate latitudes, the average temperature of the warm month is held in the range of 10-15 ° C, and the coldest -10 ° C. There are also significant daily temperature differences. For a moderate belt, the precipitation (about 1 000 mm), reaching the maximum in the autumn-winter period, and frequent ferocious storms, and the southern moderate latitudes are called "roaring forties", are characterized. Isotherm 10 ° C determines the boundaries of the northern and southern sugar belts. In the northern hemisphere, this border passes in a wide band between 50 ° C.Sh. (Labrador) and 70 ° S.Sh. (Northern Norway coast). In the southern hemisphere, the indoor zone begins closer to the equator - approximately 45-50 ° Yu.Sh. The lowest temperature (-34 ° C) was registered in the sea Weddell. 
Hydrological mode
Circulation of surface water
Powerful carriers of thermal energy are circular surface currents, located on both sides of the equator: such, for example, the Northern Passatown and South Passatowns crossing the ocean from the east to the west. The Northern Passatom Current of Small Antille Islands is divided: on the northern branch, continuing to the north-west along the shores of the large Antille Islands (Antillest current) and on the southern branch of the Small Antilian Islands in the Caribbean Sea, and then through Yucatan Strait flows into the Mexican Bay, And it comes out of it through the Floridian Strait, forming the Florida current. The latter has a speed of 10 km / h and gives the beginning of the famous flow of Gulf Stream. Gulfstream, following the American coast, at 40 ° S.Sh. As a result of the impact of Western winds and the forces of Coriolis, the East acquires, and then the northeastern direction and gets the name of the north-Atlantic flow. The main flow of water of the north-Atlantic flow runs between Iceland and the Scandinavian peninsula and poured into the northern Arctic Ocean, mitigating the climate in the European sector of the Arctic. From the Arctic Ocean, two powerful flows of cold desalinated water - the East Greenland flow passing along the eastern shore of Greenland, and the Labrador Current Current Labrador, Newfoundland and south penetrating to Cape Hatteras, squeezing Golf Stream from North America's coast. 
The South Passatom Current partially enters the northern hemisphere, and at Cape San Rocks is divided into two parts: one of them goes to the south, forming the Brazilian current, the other turns to the north, forming the Guiangic flow that goes to the Caribbean Sea. The Brazilian flow in the area of \u200b\u200bLa fees is found with a cold folkland flow (by the branch of the flow of Western winds). Near the southern end of Africa from the flow of Western winds, the cold Bengelsk for the flow and moving along the coast of South-West Africa will gradually deviate to the West. In the southern part of the Guinean Gulf, this flow closes the anticyclonic cycle of the southern trade house.
In the Atlantic Ocean there are several tiers of deep-water flows. Under the golfraim passes a powerful countercover, the main sheen of which lies at a depth of up to 3500 m, at a speed of 20 cm / s. The counterchange is a narrow stream at the bottom of the mainland slope, the formation of this flow is associated with the bottom drain of cold water from the Norwegian and Greenland seas. In the Equatorial Ocean zone, the subsurface flow of Lomonosov is open. It begins on the antilo-Guiangic countercord and reaches the Gulf of Guinea. The powerful deep Louisiana course is observed in the eastern part of the Atlantic Ocean, formed by the bottom drain flow of more salted and warm Mediterranean waters through the Gibraltar Strait.
The largest values \u200b\u200bof the tides are confined to the Atlantic Ocean, which are noted in Canada's fishing bays (in the Ungawa Bay - 12.4 m, in the Gulf of Frobisher - 16.6 m) and the United Kingdom (up to 14.4 m in Bristol Gulf). The largest magnitude of the tide in the world is fixed in Fandy Bay, on the east coast of Canada, where the maximum tide reaches 15.6-18 m.
Temperature, saline, Lyhodovka
The fluctuation of the atlantic water temperatures during the year is not large: in the equatorial-tropical belt - no more than 1-3 °, in subtropics and moderate latitudes - within 5-8 °, in the supremor latitudes - about 4 ° in the north and not more than 1 ° on South. Self warm waters - in equatorial and tropical latitudes. For example, in the Guinean bay, the temperature in the surface layer is not reduced below 26 ° C. In the northern hemisphere north of the tropics, the temperature of the surface layer is reduced (at 60 ° C.Sh. Is in the summer time 10 ° C). In the southern hemisphere, temperatures increase significantly faster and 60 ° Yu.Sh. 0 ° C oscillating. In general, the ocean in the southern hemisphere is colder than in North. In the northern hemisphere, the western part of the ocean is colder than Eastern, in South - on the contrary.
The greatest saline of surface waters in the open ocean is observed in the subtropical zone (up to 37.25), and the maximum in the Mediterranean - 39. In the equatorial zone where the maximum amount of precipitation is marked, salting decreases to 34. A sharp deterioration of water occurs in thessic areas (for example, in the mouth of the LA 18-19). 
Education in the Atlantic Ocean occurs in the Greenland and Buffinov of the seas and the pointerctic waters. The main source of icebergs in South Atlantic is the Filter Shelf Glacier at Weddell Sea. On the Greenlandic coast, the icebergs are produced with output glaciers, for example, the Jacobshaln Glacier in the Disco Island Area. Floating ice in the northern hemisphere in July reach 40 ° C.Sh. In the southern hemisphere, floating ice are present throughout the year until 55 °., Achieving maximum distribution in September-October. The total removal from the Arctic Ocean is estimated on average 900,000 km³ / year, from the Antarctica surface - 1630 km³ / year.
Water masses
Under the influence of wind and convective processes, vertical stirring of water in the Atlantic Ocean occurs, covering the surface thickness of 100 m in the southern hemisphere and up to 300 m in the tropics and equatorial latitudes. Below the surface water layer, outside the subnutrctic zone, the Antarctic intermediate water is located in the Atlantic, almost universally identified with the intermediate minimum salinity and characterized by higher in relation to the overlying water content of the biogenic elements, and extends to the north to the region of 20 ° C. At depths of 0.7-1.2 km.
A feature of the hydrological structure of the eastern part of the Northern Atlantic is the presence of an intermediate Mediterranean aqueous mass, which gradually falls to a depth of 1000 to 1250 m, moving into the deep aqueous mass. In the southern hemisphere, this water mass drops to 2500-2750 m marks and is embedded with south of 45 ° H.Sh. The main feature of these water is high salinity and temperature in relation to the surrounding waters. In the bottom layer of the Gibraltar Strait, salinity is noted to 38 ‰, temperature up to 14 ° C, but already in the Cadiz bay, where the Mediterranean waters go to the depths of its existence in the Atlantic Ocean, their salinity and temperature as a result of mixing with background waters down to 36 and 12-13 ° C, respectively. On the periphery of the distribution area, its salinity and temperature are, respectively, 35 ‰ and about 5 ° C. Under the Mediterranean water mass in the northern hemisphere, North-Atlantic deep water is formed, which falls as a result of winter cooling of relatively salted waters in the North European Basin and Sea Labrador to a depth of 2500-3000 m in the northern hemisphere and up to 3500-4000 m southern hemisphere, reaching about 50 ° Yu.Sh. North-Atlantic deep water differs from the above and underlying antarctic waters with increased salinity, temperature and oxygen content, as well as a reduced content of biogenic elements.
Antarctic bottom aqueous mass is formed on the Antarctic slope as a result of mixing the cold and severe antarctic shelf water with lighter and warm and more salted circumpolar deep waters. These waters, spreading from the sea Weddell, passing through all the orographic obstacles to 40 ° C.Sh., Have a temperature less minus 0.8ºС in the north of this sea, 0.6ºС at the equator and 1.8ºС at the Bermuda. The Arctic bottom aqueous mass has reduced salinity values \u200b\u200bcompared with the overlying waters and in the South Atlantic is characterized by an elevated content of biogenic elements.
Flora and fauna
The bottom flora of the northern part of the Atlantic is represented by brown (mainly fucoids, and in the sub-zone - laminaria and Alaria) and red algae. In the tropical zone, green (caulelepa), red (lime lithotamia) and brown algae (sargassov) predominate. In the southern hemisphere, bottom vegetation is mainly represented by laminaria. The phytoplankton of the Atlantic Ocean has 245 species: periodines, kokkolitoforids, diatoms. The latter have a clearly pronounced zonal distribution, the maximum amount of them lives in the temperate latitudes of the Northern and South Hemispheres. The most tightly population of diatoms is in the stream of the flow of Western winds. 
The distribution of the animal world of the Atlantic Ocean has a pronounced zonal character. In the subnutrctic and antarctic waters of fish have the commercial importance of not flow, Putassu and others. Benthos and plankton in the Atlantic poor and views and biomass. In the subnutrctic zone and in the adjacent band of the moderate zone of biomass reaches a maximum. In zooplankton, wearlute wraps predominate, Pteropods, in necton - from mammals of whales (blue whale), laston-either, their fish - not-data. In the tropical belt zooplankton is represented by numerous types of foraminifera and pteropod, several types of radiolearies, weakly, larvae of mollusks and fish, as well as siphonophores, various jellyfish, major charts (squid), and among bental forms - octopus. Fishing fish are represented by mackerel, tuna, sardines, in the fields of cold flows - Anchovys. Corals are confined to tropical and subtropical zones. The moderate latitudes of the northern hemisphere are characterized by an abundant life with a relatively small variety of species. Fishing fish have the greatest value to herring, cod, pike, halibut, sea bass. For zooplankton, the most characteristic of the foraminifera, the crepes. The greatest abundance of plankton in the Newfoundland Bank and the Norwegian Sea area. Deep-sea fauna is represented by crustaceans, oskulkin, specific species of fish, sponges, hydroedes. In the horror, Puerto Rico discovered several types of endemic polyhetes, isopodes and holotours. 
Ecological problems
The Atlantic Ocean is from time immemorial to the place of intensive marine fish and hunting fishery. A sharp increase in capacity and revolution in the technique of fish fishing led to a threatening scale. With the invention of the harpoon cannon in the North Atlantic, whales were mainly exterminated at the end of the XIX century. Due to the massive development of pelagic whaling fishing in Antarctic waters in the middle of the 20th century, whales here were also close to complete extermination. Since the 1985-1986 season, the International Commission on Whales was introduced a complete moratorium on commercial whaling of any species. In June 2010, at the 62nd meeting of the International Whale Commission under pressure from Japan, Iceland and Denmark moratorium was suspended.
The explosion on the Deepwater Horizon oil platform belonging to the British company BP, which occurred on April 20, 2010, is considered the largest ecological catastrophe, which ever took place at the sea. As a result of the accident in the water of the Mexican Gulf, about 5 million barrels of crude oil resulted out, 1100 miles of the coast were contaminated. The authorities introduced a ban on fishing, for the fishery there are more than a third of the entire water area of \u200b\u200bthe Mexican Gulf. As of November 2, 2010, 6,814 dead animals were collected, including 6104 birds, 609 sea turtles, 100 dolphins and other mammals, and 1 other reptile. According to the management of specially protected resources of national administration of ocean and atmospheric departments in 2010-2011, an increase in the mortality rate of cetaceans in the north of the Gulf of Mexican Bay was recorded several times compared with previous years (2002-2009). 
In the Sargasso Sea, a large garbage spot was formed from plastic and other waste, formed by ocean flows, gradually concentrating in the same area thrown into the ocean garbage.
In some areas of the Atlantic Ocean, radioactive pollution is observed. Waste of nuclear power plants and research centers are reset in the rivers and coastal waters of the seas, and sometimes in deep-water parts of the ocean. The waters of the Atlantic Ocean are heavily contaminated with radioactive waste, the North, Irish, Mediterranean Sea, Mexican, Biscay Bowls and the Atlantic Coast of the United States. Only in 1977, 7180 containers with 5,650 tons of radioactive waste were reset in the Atlantic. Agency for Protection ambient US infected sea DNA 120 miles east of the border between Maryland and Delaware. There, 14,300 cemented containers, which contained plutonium and cesium, were buried for 30 years, which contained Plutonium and Cesium, the radioactive contamination exceeded the "expected" 3-70 times. In 1970, the United States flooded 500 km from the coast of Florida, the ship "Russell-Brig", on board which was 68 tons of neuro-paralytic gas (Zarina) placed in 418 concrete containers. In 1972, in the waters of the ocean, the north of the Azores of Germany flooded 2500 metal barrels with industrial waste containing potent cyanine poisons. There are cases of rapid destruction of containers in the relatively shallow waters of the Northern and Irish seas and the strait of the La Mans with the most detrimental consequences for the fauna and the flora of the fellas. In the waters of the North Atlantic, 4 atomic submarines: 2 Soviet (in the Biscay bay and open part of the ocean) and 2 American (off the coast of the United States and in the open part of the ocean).
The coast of the Atlantic Ocean
On the shores of the Atlantic Ocean and the seas that are part of its composition are states and dependent areas:
- In Europe (from north to south): Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, the Russian Federation, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Federal Republic of Germany, Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, United Kingdom, Ireland, Isle of Man (UK Possession), Jersey (United Kingdom Ownership), France, Spain, Portugal, Gibraltar (Possession of Great Britain), Italy, Malta, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Abkhazia (UN is not recognized), Georgia;
- In Asia: Cyprus, the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (UN), Akrotiri and Deckelia (UK Ownership), Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestinian Authority (UN is not recognized);
- In Africa: Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Sahara Arab Democratic Republic (not recognized by the UN), Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire , Ghana, Benin, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, San Tome and Principe, Gabon, Republic of Congo, Angola, Democratic Republic of Congo, Namibia, South Africa, Bouwa Island (Norway, Holy Islands, Ascension and Tristan da Cunya (Possession of Great Britain);
- In South America (from the south to north): Chile, Argentina, South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands (UK Ownership), Falkland Islands (UK Possession), Uruguay, Brazil, Suriname, Guyana, Venezuela, Colombia, Panama;
- In the Caribbean: American Virgin Islands (USA), Anguilla (British possession), Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, British Virgin Islands (UK Possession), Haiti, Grenada, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Cayman Islands (Possession of Great Britain) , Cuba, Montserrat (United Kingdom), Navassas (USA), Puerto Rico (USA), Saint Vincent and Grenadines, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Turks and Caicos (Possession of Great Britain), Trinidad and Tobago , Jamaica;
- In North America: Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Guatemala, Belize, Mexico, United States of America, Bermuda (Possession of Great Britain), Canada.
History of the study of the Atlantic Ocean by Europeans
Long before the era of the great geographical discoveries, the expanses of the Atlantic korozdili numerous vessels. Another 4000 years before our era, the peoples of Phenicia led maritime trade with residents of the Islands of the Mediterranean Sea. At a later time, from the 6th century BC, the Phoenicians, according to the testimony of Greek historian Herodotus, made campaigns around Africa, and through the Gibraltar Strait and around the Pyrenean Peninsula reached the British islands. By VI century BC Ancient Greece, having an enormous military merchant fleet for that time, swam to the shores of England and Scandinavia, in the Baltic Sea and to the Western Coast of Africa. In the X-XI Art. new page Vikings entered the study of the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean. According to the majority of researchers of pre-columbotic discoveries, the Scandinavian Vikings first and once twisted the ocean, reaching the banks of the American continent (they called it in Winland) and opening Greenland and Labrador.
In the XV century, Spanish and Portuguese navigators began to make distant swimming in search of ways to India and China. In 1488, the Portuguese Expedition Bartolome Diash reached the Cape of Good Hope and rented Africa from the south. In 1492, the expedition of Christopher Columbus caused many Islands of the Caribbean and a huge mainland later called America. In 1497, Vasco da Gama passed from Europe to India, having encouraged Africa from the south. In 1520, Fernan Magellan, during the first world swimming, passed by the Magellan Strait from the Atlantic in the Pacific Ocean. At the end of the 15th century, rivalry between Spain and Portugal for domination in the Atlantic was so much so that the conflict was forced to intervene the Vatican. In 1494, a contract was signed, which was established at 48-49 ° W. N. "Papal Meridian." All the lands west of it were given to Spain, and to the East - Portugal. In the XVI century, as the colonial wealth arises, the wave of Atlantic began to regularly boil ships, transporting gold, silver, precious stones, pepper, cocoa and sugar to Europe. In America, weapons, tissues, alcohol, products and slaves for cotton plantations and sugar cane delivered to America. It is not surprising that in the XVI-XVII Art. Pirate fishery and kaperism flourished in these parts, and many famous pirates, such as John Hawkins, Francis Drake and Henry Morgan, entered their names in history. The South Border of the Atlantic Ocean (Mainland Antarctica) was opened in 1819-1821 by F. F. F. Bellinshausen and M. P. Lazarev, the first Russian Antarctic Expedition. 
The first attempts to study the seabed were undertaken in 1779 near the shores of Denmark, and the first Russian round-the-world expedition was launched in 1803-1806 in 1803-1806. Measurements of temperature at various depths were carried out by J. Cook (1772), O. Sosyur (1780 year), and others. Participants in subsequent trips conducted measurements of temperature and specific weight of water at different depths, took samples of transparency of water and installed the presence of underwater flows. The assembled material made it possible to make a map of Golf Stream (B. Franklin, 1770), the map of the depths of the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean (M. F. Mori, 1854), as well as windows and ocean flows (M. F. Mori, 1849-1860) and hold Other studies.
From 1872 to 1876, the first scientific ocean expedition was held in the English sail-vapor Corway "Challenger", new data on the composition of the ocean, about the plant and animal worlds, about the rank of bottom and soil, was composed of the first map of the depths of the ocean and the first collection was collected deep-water animals, as a result of which the extensive material was collected, published in 50 volumes. For her, the expedition was followed on the Russian sail-screw Corvete "Vityaz" (1886-1889), on the German courts "Valdivia" (1898-1899) and "Gauss" (1901-1903) and others. The largest work was carried out on the English ship "Discovery II" (since 1931), thanks to which oceanographic and hydrobiological studies were performed in the open part of the South Atlantic at large depths. Within the framework of the International Geophysical Year (1957-1958), international forces (especially the United States and the USSR) conducted studies, as a result of which new baaptic and marine navigation maps of the Atlantic Ocean were compiled. The intergovernmental oceanographic commission in 1963-1964 was held a major expedition to study the equatorial and tropical ocean zone, in which the USSR took part (on the ships "Vityaz", Mikhail Lomonosov, "Academician Kurchatov" and others), USA, Brazil and others countries.
In recent decades, numerous ocean measurements were carried out with space satellites. The result was released in 1994 by the American National Center for Geophysical Data Batymetric Oceans Atlas with 3-4 km permission and depth accuracy of ± 100 m.
Economic importance
Fishing and marine crafts
The Atlantic Ocean gives 2/5 world catch and its share decreases over the years. In the subnutrctic and antarctic waters, commercial importance has not flow, Putassu and others, in a tropical belt - Mackerel, Tuns, Sardine, in the areas of cold flows - anchovies, in moderate latitudes of the northern hemisphere - herring, cod, pike, palus, sea bass. In the 1970s, due to the fleet of some species of fish, the volume of the fishery decreased sharply, but after the introduction of strict limits, fish reserves are gradually restored. In the Atlantic Ocean pool, there are several international fisheries conventions that are intended to be effective and rational use of biological resources, based on the application of scientifically based measures for the regulation of fishery.
Transport routes
The Atlantic Ocean occupies a leading place in global shipping. Most of the paths leads from Europe to North America. The main shipping strands of the Atlantic Ocean: Bosphorus and Dardanelles, Gibraltar, La Mans, Pa de Calais, Baltic Straits (Skagerrak, Kattegat, Eresund, Big and Small Blouth), Danish, Florida. The Atlantic Ocean is connected to the quiet ocean with an artificial Panaman channel, a breakthrough between North and South America through the Panaman Isthmus, as well as with the Indian Ocean artificial Suez Canal through the Mediterranean Sea. Largest ports: St. Petersburg (General Loads, Petroleum products, Metals, Forest Loads, Containers, Coal, Ore, Chemical Loads, Screw, Hamburg (Machinery and Equipment, Chemicals, Raw materials for metallurgy, oil, Wool, forest, Food) , Bremen, Rotterdam (Oil, Natural Gas, Ore, Fertilizers, Equipment, Food), Antwerp, Gavr (Oil, Equipment), Philikstow, Valencia, Algeciras, Barcelona, \u200b\u200bMarseille (Oil, Ruda, Grain, Metals, Chemical Loads, Sugar , fruits and vegetables, wine), joy-tauro, Marsachlokk, Istanbul, Odessa (raw sugar, containers), Mariupol (coal, ore, grain, containers, petroleum products, metals, forest, food), Novorossiysk (oil, ore, Cement, Grain, Metals, Equipment, Food), Batumi (Oil, General and Equal Loads, Food), Beirut (exportation: Phosphorites, Fruits, Vegetables, Wool, Forest, Cement, Importation: Machinery, Fertilizers, Cast iron, Building materials, Food), Port Said, Alexandria (export: cotton, rice, ore, importation: equipment, metals, petroleum products, fertilizers), Casablanca (exportation: phosphorites, ores, citrus fruits, cork, food, importation: equipment, fabrics, petroleum products), Dakar (earthworm, dates, cotton, cattle, fish, ore , Importation: Equipment, Petroleum products, Food), Cape Town, Buenos Aires (exportation: Wool, Meat, Grain, Leather, Vegetable oil, Linen seed, Cotton, Importation: Equipment, Iron Ore, Coal, Oil, Industrial Goods), Santus , Rio de Janeiro (exportation: iron ore, cast iron, coffee, cotton, sugar, cocoa beans, lumber, meat, wool, leather, import: petroleum products, equipment, coal, grain, cement, food), Houston (oil , Grain, Sulfur, Equipment), New Orleans (ore, coal, Building raw materials, Cars, Grain, Rental, Equipment, coffee, Fruit, Food), Savannah, New York (General Loads, Oil, Chemical Loads, Equipment, Cellulose , paper, coffee, sugar, metals), Montreal (Grain, Oil, Cement, Coal, Forest, Metals, Paper, Asbes t, weapons, fish, wheat, equipment, cotton, wool). 
Aviation message is played by the dominant role in the passenger communication between Europe and North America through the Atlantic Ocean. Most of the transatlantic lines take place in the North Atlantic through Iceland and Newfoundland. Another message goes through Lisbon, Azores and Bermuda. Airways from Europe to South America passes through Lisbon, Dakar and then through the narrowest part of the Atlantic Ocean in Rio de Janeiro. Airlines from the USA to Africa pass through the Bahamas, Dakar and Robertsport. On the shores of the Atlantic Ocean are cosmodromes: Cape Canaveral (USA), Kuru (French Guiana), Alcantara (Brazil).
Minerals
Mining mining, primarily oil and gas, is carried out on the mainland shelves. Oil is mined on the shelves of the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, the North Sea, the Biscay Bay, the Mediterranean Sea, the Guinean Bay. Natural gas is also underway on the North Sea shelf. In the Gulf of Mexico, there are industrial mining of sulfur, and at the island of Newfoundland - iron ore. Diamonds are mined from marine plaques on the mainland shelf of South Africa. The following by the value group of mineral resources form coastal fields of titanium, zirconium, tin, phosphorites, monazita and amber. From the seabed also mining coal, barite, sand, pebbles and limestone.
In the shores of the seas of the Atlantic Ocean, tidal power plants were built: "La Rans" on the Ranss River in France, "Annapolis" in the Gulf of Fandy in Canada, Hammerfest in Norway.
Recreational resources
The recreational resources of the Atlantic Ocean are characterized by a significant variety. The main countries of the formation of outbound tourism in this region are formed in Europe (Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Netherlands, Belgium, Austria, Sweden, Russian Federation, Switzerland and Spain), North (USA and Canada) and South America. The main recreational zones: the Mediterranean coast of Southern Europe and North Africa, the coast of the Baltic and Black Seas, the Florida Peninsula, Cuba Islands, Haiti, Bahamas, Areas of Cities and urban agglomerations of the Atlantic Coast of North and South America. 
Recently, the popularity of countries of the Mediterranean, as Turkey, Croatia, Egypt, Tunisia and Morocco is growing. Among the Atlantic Ocean countries with the highest flow of tourists (according to 2010, the World Tourism Organization) are allocated: France (77 million visits per year), USA (60 million), Spain (53 million), Italy (44 million), United Kingdom (28 Million), Turkey (27 million), Mexico (22 million), Ukraine (21 million), Russian Federation (20 million), Canada (16 million), Greece (15 million), Egypt (14 million), Poland (12 million ), Netherlands (11 million), Morocco (9 million), Denmark (9 million), South Africa (8 million), Syria (8 million), Tunisia (7 million), Belgium (7 million), Portugal (7 million) , Bulgaria (6 million), Argentina (5 million), Brazil (5 million).
(Visited 234 Times, 1 Visits Today)
It covers an area of \u200b\u200b92 million km. It collects fresh water from the most significant part of the sushi and stands out among other oceans by the fact that both polar regions of the Earth connect in the form of a wide strait. The middle-atlantic ridge passes in the center of the Atlantic. This is an instability belt. Separate vertices of this ridge rise above the water in the form. Among them are the largest -.
The southern tropical part of the ocean is under the influence of the South-Eastern Passat. The sky above this part is slightly tinted with cumulus clouds similar to cotton. This is the only place in the Atlantic, where there. The color of the water in this part of the ocean ranges from the dark blue to the bright green (near). Water is green when approaching, as well as the southern shores. The tropical part of the south of the Atlantic is very rich in life: Plankton's density there is 16 thousand individuals on a liter; There is an abundance of volatile fish, sharks and other predatory fish. There are no coral builders in the southern part of the Atlantic: they were supplanted from here. Many researchers notice that cold flows in this part of the ocean richer life than warm.
: 34-37.3.
Additional Information : The Atlantic Ocean received its name from the Atlantic Mountains located in the North-West Africa, on another version - from the mythical continent of Atlantis, on the third - on behalf of Titan Atlas (Atlanta); The Atlantic Ocean is conventionally divided into the northern and southern regions, the boundary between which runs along the equator.
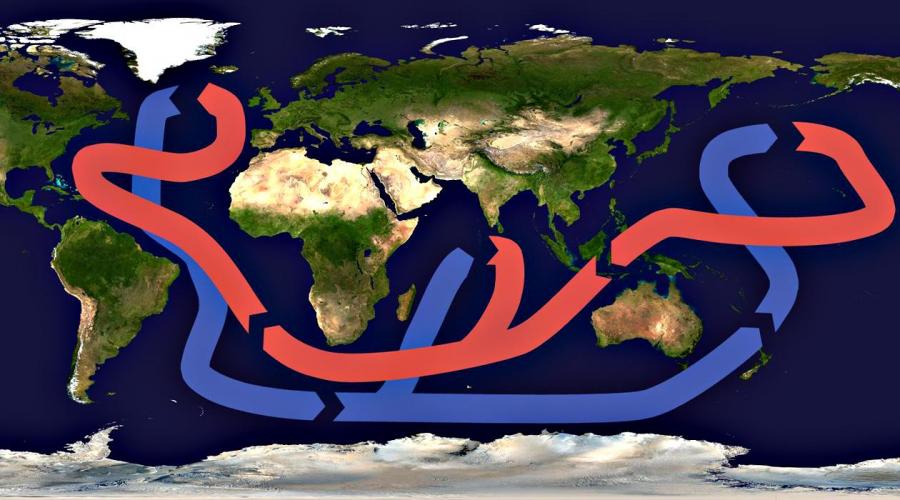
Many know about Golf Stream, which, carrying huge masses of water from equatorial latitudes to polar, literally warms the north of Western Europe and Scandinavia. But few people know that there are other warm and cold flow of the Atlantic Ocean. How do they affect the climate of coastal areas? This will tell our article. In fact, a lot of currents in the Atlantic. Briefly list them for general development. This is Western Greenland, Angolan, Antilles, Bengelskoe, Guinean, Lomonosov, Brazilian, Guiangskoye, Azores, Golfstream, Irminger, Canary, East Icelandic, Labrador, Portuguese, North Atlantic, Florida, Falkland, North Equatorial, South Commercial, and Equatorial counterchange . Not all of them have a great influence on the climate. Some of them are generally part or fragments of the main, larger currents. That's what they are talking about our article.
Why flows are formed
In the World Ocean, the circulation of large invisible "rivers without shores" is constantly underway. Water is generally very dynamic element. But with rivers everything is clear: they flow from the source to the mouth due to the difference in altitudes between these points. But what makes the huge masses of water within the ocean? Of the many reasons, two are the main: trade-wind wind and changes in atmospheric pressure. Because of this flow, divided into drift and bar designates. The first are formed by trade winds - continuing in the same winds. Most such trends. Mighty rivers put in the sea a large amount of water other than marine density and temperature. Such flows are called stock, gravitational and friction. It should take into account the greater length from the north to the south, which has the Atlantic Ocean. The flows in this water area therefore have more meridional than the latitudinal direction.

What is Passat
The wind is the main reason for the movement of vast masses of water in the world ocean. But what is the trade winds? The answer should be sought in the equatorial areas. There, the air warms up more than in other latitudes. It rises up and on the upper layers of the troposphere spreads towards two poles. But already on the latitude of 30 degrees, thoroughly cooled, it goes down. Thus, a circulation of air masses is created. In the region of the equator, a low pressure zone occurs, and in tropical latitudes - high. And here manifests itself the rotation of the earth around the axis. If it were not for it, the trade winds would blow from the tropics of both hemispheres to the equator. But, since our planet rotates, the wind deviates, acquiring the Western direction. So the Passats form the main flow of the Atlantic Ocean. In the northern hemisphere, they move clockwise, and in South - against. This is because in the first case, the Passats blow from the northeast, and in the second - from the southeast.

Impact on climate
Based on the fact that the main flows are born in the equatorial and tropical regions, it would be reasonable to assume that they are all warm. But this is not always happening. The warm flow in the Atlantic Ocean, reaching the polar latitudes, does not fade, but, making a smooth circle, reversed, but it is already pretty cooling. This can be observed on the example of Golf Stream. It carries warm masses of water from Sargassov Sea to the north of Europe. Then, under the action of rotation of the Earth, he deviates to the West. Under the name of the Labrador current, he descends along the shore of the North American continent south, cooling the seaside regions of Canada. It should be said that with warm and cold, these mass of water are conditionally called relative to the ambient temperature. For example, in the North County in winter, the temperature is only +2 ° C, and in the summer - maximum +8 ° C. But it is called warm, as water in the Barents Sea is even colder.

The main flow of the Atlantic in the northern hemisphere
Here, of course, it is impossible not to mention Golf Stream. But the other flows passing through the Atlantic Ocean have an important impact on the climate of nearby territories. Green Cape (Africa) is born by the Northeast Passat. He drives huge warming masses to the west. Crossing the Atlantic Ocean, they are connected to the Antilles and Guiancondes. This enhanced jet moves to the Caribbean Sea. After this water rushed to the north. This continuous movement clockwise is called the warm North Atlantic flow. The edge of it in high latitudes is indefinite, blurred, and the equator is clearer.

Mysterious "Bay Current" (Golf-Stream)
It is so called the current of the Atlantic Ocean, without which Scandinavia and Iceland would turn, on the basis of their proximity to the pole, to the edge of eternal snow. Previously, they thought Golf Stream was born in the Gulf of Mexico. Hence the name. In fact, only a small part of the golfustrium follows from the Gulf of Mexico. The main flow comes from Sargasso Sea. What is the mysteriousness of Golf Stream? In the fact that he, despite the rotation of the Earth, does not flow from the West to the East, but in the opposite direction. Its power exceeds the drain of all the planet rivers. The speed of the golfustrium is impressive - two and a half meters per second on the surface. Currently traced at a depth of 800 meters. And the width of the flow is 110-120 kilometers. Due to the high flow rate, water from equatorial latitudes do not have time to cool. The surface layer has a temperature of +25 degrees, which, of course plays a primary role in the formation of the climate of Western Europe. The Gulf Stream Mystery consists also in the fact that it does not wash the mainland anywhere. Between it and the shore there is always a strip of cold water.
Atlantic Ocean: the currents of the southern hemisphere
From the African continent to the American Passat drives a jet, which, due to low pressure in the Equatorial region, begins to deviate to the south. So begins a similar northern cycle. However, the southern trade house is moving counterclockwise. It also passes through the entire Atlantic Ocean. The flow of Guiangie, Brazilian (warm), Falkland, Bengelsk (Cold) are part of this cycle.
