A selection of material for preparing for the exam in biology in the section "Plants" material for preparing for the exam (gia) in biology (grade 11) on the topic. Botany. Higher and lower plants Preparing for the exam plants
Read also
Let's first define the main factors that characterize the organisms of this kingdom.
Features of the cellular structure:
1.The presence of chloroplasts in the cell.
This organelle determines everything in the plant organism: physiological processes, life cycles, and ecological role.

2. Vacuoles.

3. Cell wall(reserve nutrient - carbohydrates (most often starch or cellulose)) - an additional membrane, a thickening of the cell membrane. The main role is a protective and small supply of substances.

Plant physiology
Breath: oxygen, like all other living organisms.
Nutrition: as we mentioned above, plants - autotrophs - produce food for themselves.
When you read school textbooks, you get the impression that, besides light, water and carbon dioxide, plants do not need anything else.
Talk to gardeners, your hair stands on end - some plants need more fertilized soil, others less alkaline, acidic, sandy….
It turns out that plants feed on no air and water ...

Plants need nutrients and they get them from the soil.
These are both organic and inorganic (mineral) substances.
Growth and development
Another distinctive feature of plants, common with fungi, but absent in animals - growth throughout life.
Reproduction:
1. sexual - with the help of gametes (sex cells);
2. asexual, vegetative - with the help of body parts;
3. asexual, with the help of spores (only in spore plants).
Plant taxonomy
Plant departments:
Algae Department
It does not matter, unicellular or multicellular alga - neither tissues nor organs!

Spore Plants Department
They are already referred to as the highest, tk. both tissues and organs are available. By name and development - reproduction proceeds with alternation of generations - asexual (spore) and sexual (gametophyte).
There are no flowers, no fruits, no seeds.
Seed Plants Division
Complex structure and seed reproduction.
Gymnosperms- the reproductive organ is a lump.
Angiosperms- reproductive organs - flower and fruit.
The evolution of plants went exactly in this way - from protozoa to angiosperms:

Plants are eukaryotic photosynthetic autotrophic organisms. The plant kingdom has about 500 thousand species.
The listed differences between plants and animals are not absolute. Traits of animal organization are often found in lower plants, which correspond to the early stages of evolutionary development. For example, the ability to both autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition (euglena green). More highly organized plants differ quite clearly from animals.
Plants are divided into lower and higher. Have lower plants the body (thallus or thallus) is not dissected into tissues and organs. These include Red Algae (Bagryanka), True Algae, and Lichens. Have higher plants the body is divided into organs (root, stem, leaf) formed by differentiated tissues. Higher plants include Mossy, Lopid, Horsetail, Fern, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms (Flowering). The first four sections are settled by spores ( controversial
), the last two - with the help of seeds ( seed
).
Reproduction of plants. All higher plants are characterized by alternation in the life cycle of sexual and asexual reproduction and the associated alternation of generations (developmental phases) - haploid (n) (gametophyte) and diploid (2n) (sporophyte). On sporophyte
saccular formations appear - sporangia (organs of asexual reproduction), in which, as a result sporogenesis
accompanied by meiotic division, haploid disputes
... From the dispute develops gametophyte
... Special sexual structures are formed on it - gametangia
(organs of sexual reproduction), in which gametes
.
The male genital organs, where sperm are formed, are called antheridia
, the female genital organs, where the eggs are formed, are called archegonia
... If both archegonia and antheridia develop on the gametophyte, then it is called bisexual
, if only antheridia, then male
, if only archegonia, then female.
When gametes merge, zygote
... A sporophyte develops from the zygote.
Department of Angiosperms (Flowering)
Angiosperms- Evolutionarily the youngest and most numerous group of plants. The department includes about 250 thousand species. Angiosperms grow in all climatic zones, constitute the bulk of the plant matter of the biosphere and are the most important producers (producers) of organic matter on land.
The dominant role of flowering plants is due to a number of progressive features:
- Emergence flower- an organ that combines the functions of asexual reproduction (spore formation) and sexual (seed formation).
- Formation in the composition of a flower ovaries, which contains the ovules (ovules) and protects them from the adverse effects of the environment.
- Formation from the ovary fetus: the seeds are inside the fruit and are therefore protected (covered) by the pericarp. In addition, the fruit allows the use of various agents for the spread of seeds (insects, birds, bats, as well as currents of air and water).
- Double fertilization, as a result of which a diploid embryo and a triploid (and not haploid, as in gymnosperms) endosperm are formed.
- Maximum reduction of gametophyte. Male gametophyte - a pollen grain - consists of two cells: vegetative and generative, which divides to form two sperm. The female gametophyte consists of eight cells of the embryo sac, one of which becomes the ovum.
- Reproduction and seeds, and vegetative organs.
- Complication and high degree of differentiation of organs and tissues. In particular, the most perfect conducting system: the xylem is represented by vessels, not tracheids; in the phloem, sieve tubes have a segmented structure, and satellite cells appear.
- Rapid course of growth and development processes in annual forms.
- Big variety of life forms: trees, shrubs, shrubs, dwarf shrubs, perennial grasses, annual grasses, etc.
- Can form complex multi-tiered communities due to the wide variety of life forms.
The importance of angiosperms in human life can hardly be overestimated. Almost all cultivated plants belong to this department. Angiosperm wood is used in industry, construction, papermaking, furniture, etc. Many flowering plants are used in medicine.
section "Plants"Questions that need to be answered in detail.
1. In the leaves of plants, the process of photosynthesis is intensive. Does it occur in ripe and unripe fruits? Explain the answer.
2. What are the characteristics of conifers?
1) reproduction by seeds that lie openly on the scales of cones
2) no aquatic environment is needed for fertilization
3) leaves are scaly or needle-like, covered with a waxy bloom
3. What are the main differences between mosses and ferns?
1) have neither roots nor rhizomes.
2) in mosses, the haploid phase of development (gametophyte) prevails over the diploid phase (sporophyte). Moss sporangia are bolls with spores, while ferns have sori located on the underside of leaves.
3) low-organized mosses do not yet have division into organs. More organized bryophytes have rhizoids, stems and leaves.
4) ferns have rhizomes, stems, leaves, fully formed conductive tissues
4. It is known that in sphagnum bogs, despite the large amount of moisture, water is inaccessible to many plants. What is the reason for this?
2) acidification of water and soil of bogs also interferes with root growth;
5. What is the peculiarity of the nutrition of unicellular algae?
The peculiarity is that they are able to absorb dissolved organic matter through the pores of the shell.
6. What characteristic signs plants do you know?
Typical plant features:
1. Plant cells are covered with a thick, dense cellulose cell wall (membrane), which gives them shape.
2. Cells contain plastids, which contain the green pigment chlorophyll. It is a photosynthetic pigment.
3. Plants are characterized by the process of photosynthesis - the formation of organic substances from inorganic ones using solar energy. Therefore, according to the method of nutrition, most plants are autotrophs.
4. Plant cells contain vacuoles with cell sap, they regulate the osmotic flow of water into the cell, and they also accumulate reserve nutrients and metabolic products of the cell.
7. What is the significance of photosynthesis for life on Earth?
1) photosynthesis provides all living organisms with the organic substances they need.
2) in the course of photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy available to living organisms.
3) in the light phase of photosynthesis, a by-product is released - molecular oxygen, which is necessary for respiration for most organisms.
8. Why do many seeds not germinate when there is an excess of water in the soil?
1) With an excess of water in the soil, there is a lack of oxygen, which is necessary for the respiration of the plant.
2) Germinating seeds of most plants receive a significant part of oxygen from free spaces of the soil, and not from water.
9. Why did angiosperms occupy a dominant position on Earth?
1) the life forms of angiosperms are represented by trees, shrubs, grasses, which determines their greatest ecological plasticity.
2) vegetative organs (roots, leaves, shoots) have numerous modifications and
3) are the most specialized in structure and function.
4) the seeds of angiosperms are protected by the pericarp, which contributes to their better preservation and distribution.
5) no water is required for fertilization, and pollination methods are very diverse (insects, wind, self-pollination, etc.).
6) they are spread by wind, water, animals or humans.
10. What role do stomata play in plant life?
1) stomata - a highly specialized formation of the plant epidermis, consisting of two guard cells and an intercellular space (stomatal gap) between them.
2) transpiration and gas exchange are carried out through the stomata. Transpiration is the evaporation of water by a plant.
3) transpiration regulates the water and temperature regime of the plant.
11. How can you explain that multicellular plants are composed of several types of tissues?
1) with the advent of the multicellular organisms, various functions appeared in plant organs, and these functions could be performed only by special formations - tissues.
2) to organs that are far from each other, it is necessary to conduct substances, this is done by conductive tissues.
3) excess substances accumulate in the cells of the main tissue, etc.
12. It is known that before transplanting young plants into the ground, they are picked (pinched off the tip of the main root). Why do they do this?
1) when picking plants, the growth of adventitious and lateral roots is activated;
2) due to an increase in the total number of adventitious and lateral roots, the mineral nutrition of the plant improves, which stimulates its growth.
13. Find errors in the text provided, correct them, indicate the numbers of the sentences in which they are made, write down these sentences of errors.
1. A flower is an organ of reproduction of angiosperms.
2. The flower is a modified leaf.
3. The functions of a flower are sexual and asexual reproduction.
4. The flower is connected to the stem by a peduncle.
5. The flower has pistils and stamens.
1) a flower is a modified shoot;
2) a flower is an organ of sexual reproduction, it has nothing to do with asexual reproduction;
3) not all flowers contain pistils and stamens, there are dioecious (pistillate and staminate flowers), in addition, there may be one pistil in a flower.
14. With the introduction of potatoes into cultivation, potato riots arose in Russia. Why the peasants did not want to grow this plant
15. What are the main features of the structure of plant cells?
1) the presence of a rigid cellulose cell wall;
2) the presence of vacuoles with cell sap;
3) the presence of plastids.
16. What are the main distinguishing features of higher plants in comparison with lower ones?
1) adaptability to reproduction in a terrestrial environment;
2) the presence of well-differentiated tissues and organs;
3) organs of reproduction are multicellular.
17. Find errors in the text, indicate the numbers of the sentences in which they are allowed. Explain them.
1.Two divisions of angiosperms are distinguished: monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous.
2. Dicotyledonous plants evolved from monocotyledons and they have many similarities.
3.The embryo of dicotyledons consists of two cotyledons.
4. Leaf blades of dicotyledons, usually with parallel and arcuate venation.
5. Monocotyledonous plants usually have fibrous roots, a three-membered type of flower structure.
6. These are mainly herbaceous plants.
18. Gardeners, when picking cabbage seedlings, pinch the top of the main root, and when propagating currant bushes, they use stem cuttings, on which adventitious roots develop. Both of these flowering plants belong to the dicotyledonous class. Explain what type of root system will be found in cabbage grown from this seedling, and what type of root system will be in currant grown from stem cuttings.
Response elements:
19. The flowers of many angiosperms are pollinated by insects. Explain the mutual benefits of cross-pollination for insects and plants.
Response elements:
1) For plants: thanks to insects, the probability of pollination increases, the possibility of the offspring acquiring new traits increases (variability and better
20. What tissue of flowering plants connects its organs into a single whole?
Conductive tissue (xylem and phloem)
21. What are the characteristics of angiosperms?
Response elements:
1) the presence of a flower
2) the presence of fruits with seeds
3) double fertilization
4) great variety ecological forms and groups
23.What is the purpose of whitewashing trunks and large branches fruit trees?
To protect against sunburn and from pests.
24. What are the characteristics of the plant kingdom?
1) The presence of chloroplasts in the cells, in which photosynthesis occurs
2) The presence in the cell of a membrane of fiber and vacuoles with cell juice
3) They grow throughout life, most do not move from one place to another.
25. Find errors in the text provided. Indicate the numbers of the sentences in which mistakes were made, explain them.
Response elements: mistakes were made in sentences:
1) 2 - among the mushrooms there are also unicellular ones, for example, yeast;
2) 3 - autotrophs are absent among fungi (since their cells do not have chlorophyll);
3) 4 - the cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin, not cellulose.
26. Name at least 3 features of land plants that allowed them to be the first to master the land. Justify the answer.
Response elements:
1) the emergence of integumentary tissue - the epidermis with stomata, which helps to protect against evaporation;
2) the emergence of a poorly developed conducting system that ensures the transport of substances;
3) the development of mechanical tissue that performs a supporting function;
4) the formation of rhizoids, with the help of which they were fixed in the soil.
27. What processes ensure the movement of water and mineral substances by plant? Explain the answer.
Response elements:
28. Why does plowing the soil improve the living conditions of cultivated plants?
Response elements:
29. What are the characteristic features of the mushroom kingdom?
Response elements:
1) the body of the mushrooms consists of filaments - hyphae, which form the mycelium;
2) reproduce sexually and asexually (by spores, mycelium, budding);
3) grow throughout life;
4) cell membranes contain a chitin-like substance, a reserve nutrient - glycogen.
30. Explain through which tissues and how the transport of substances is carried out in angiosperms.
Response elements:
31. Find errors in the text provided, correct them, indicate the numbers of the sentences in which they are made, write down these sentences without errors.
Response elements:
32. In the 17th century, the Dutch scientist Van Helmont conducted an experiment. He planted a small willow in a tub of soil, after weighing the plant and soil, and only watered it for several years. After 5 years, the scientist weighed the plant again. Its weight has increased by 63.7 kg, while the weight of the soil has decreased by only 0.06 kg. Explain, due to what there was an increase in the mass of the plant, what substances from the external environment provided this increase.
Response elements:
33. What is the difference between root crops and root tubers?
34. What is the significance for plants of middle latitudes of leaf fall?
What are the distinctive features of brown algae?
Response elements:
2) the main storage product is kelp;
3) there are mobile stages in the life cycle;
4) all brown algae are multicellular.
35. What are the ways of spreading fruits and seeds?
Response elements:
1) with the help of the wind;
2) using water;
3) with the help of animals and humans;
4) self-spreading.
36. What is the difference between the embryos of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants?
Response elements:
1) in dicotyledons, the embryo usually has two cotyledons, in monocots - one;
2) in dicotyledons, the embryo is symmetric - the bud occupies an apical position, and the cotyledons are located on the sides of the embryo, in monocots - the embryo is asymmetric - the cotyledon occupies an apical position, and the bud is located on the side;
3) in dicotyledons, cotyledons usually germinate aboveground, in monocots, usually underground.
37. In what is the ecological significance of nodule bacteria for plants?
Nodule bacteria form symbiosis with legumes and are involved in fixing atmospheric nitrogen into mineral compounds available to plants.
38. Why are lichens very hardy?
The endurance of lichens is explained by the possibility of both autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition, as well as the ability to fall into a state of suspended animation, in which the body is severely dehydrated.
39. How does a person use bacteria?
Response elements:
1) in treatment facilities;
2) in everyday life and in the food industry;
3) in microbiological synthesis;
4) to obtain a number of medicines.
40. How are mushrooms different from plants?
Response elements:
1) heterotrophic diet;
2) storage nutrient glycogen;
3) the presence of chitin in the cell walls.
41. What is called double fertilization?
42. Name features kingdom of mushrooms from the kingdom of plants.
Response elements:
1) fungi are heterotrophs, not capable of photosynthesis
2) mushrooms are different cellular structure: do not have chloroplasts, the cell wall contains chitin, the reserve nutrient is glycogen;
3) the body of the mushrooms is formed by hyphae.
43. Why the psilophytes were the first to master the land
Response elements:
1) the appearance of integumentary tissue - the epidermis with stomata - contributing to protection against evaporation;
2) the emergence of a poorly developed conducting system that ensures the transport of substances;
3) the appearance of mechanical tissue that performs a supporting function;
4) the formation of rhizoids, with the help of which they were fixed in the soil.
44. What harm does a tinder fungus bring to a birch tree?
45. What are the similarities and differences between the fruits of plants of the Asteraceae family and the Cereals family?
Response elements: common features:
1) single-seeded dry non-opening fruits;
differences:
2) in cereals, the fruit is a caryopsis, and in Compositae - a caryopsis;
3) in the caryopsis, the seed coat grows together with the pericarp, and in the achene, the seed lies freely, the fruits may have crests, parachutes, attachments.
46. What are the adaptations of plants to life in dry conditions?
Response elements:
47. Find mistakes in this student's answer and comment on them.
Plants of the legume family have a regular five-membered flower, a pod fruit and a fibrous root system.
Response elements:
1) a five-membered butterfly flower, irregular: an unpaired sail petal, paired oar petals and fused petals - a boat;
2) rod-type root system;
3) the fruit is a bean, not a pod.
48. What is the significance in the life of plants of putting hives on buckwheat fields by beekeepers?
Prove that the lily of the valley rhizome is a modified shoot.
Response elements:
49. What is the significance of various flowers in the inflorescences of plants of the Asteraceae family?
Response elements: different types flowers in the inflorescence of Compositae perform various functions:
1) attraction of insects - pseudo-lingual and funnel-shaped;
2) seed formation - tubular and ligulate flowers.
50. Explain why seedlings do not develop when small seeds are sown at great depths.
Small seeds contain little nutrients is not enough for the seedling to reach the soil surface.
51. What features of the structure of the fruit - drupes ensure the spread of seeds of many representatives of plants of the Rosaceae family?
Response elements:
1) drupe - a single-seeded fruit with brightly colored juicy pulp, which attracts animals;
2) drupes are eaten by birds or mammals, while the seeds, covered with a lignified part of the pericarp, are not digested in the digestive canal of the animal and are removed with droppings
52. Why does potato yield increase after hilling?
53. In what processes of life of plants does water participate?
54. Why can lichens live in barren places where other organisms cannot survive?
Lichen is a symbiotic organism. Its body (thallus) is composed of fungus and algae. Lichens can grow on rocks, walls, sand. They don't need soil. The fungus hyphae absorb moisture from rain, dew and fog over their entire surface. Single-celled algae containing chlorophyll produce organic matter through photosynthesis.
55. Why did the emergence of plants from water to land become possible with the appearance of tissues?
On land, the living conditions of plants are more severe than in water. To adapt to them, specialized fabrics are needed. Thus, mechanical tissue supports the plant. The cover fabric protects against drying out and sunburn. The suction cloth ensures that water is drawn from the soil. The conductive tissue spreads water and dissolved substances throughout the plant. Thus, these fabrics compensate for the disadvantages of the ground-air environment: low density, lack of water, high intensity of illumination.
56. What is the purpose of pinching the main root of some cultivated plants?
To stimulate the growth of adventitious and lateral roots, developing in the upper, more fertile soil layer.
57. What are spores of plants and fungi?
Reproduction by sporulation is characteristic of algae, mosses, ferns, and fungi. Spores are special cells, often covered with a dense membrane that protects them from adverse external influences. Usually, spores are formed in large numbers and have negligible weight, which facilitates their spread by wind and animals. Due to its small size, the spore contains only a minimal supply of nutrients. Due to the fact that many spores do not get into a place suitable for germination, their losses are very high. In favorable environmental conditions, the shell of the spore opens, the cell divides many times and gives rise to a new organism.
58. Read the text "Fertilization in Flowering Plants" and look for sentences that contain biological errors. Write down the numbers of these sentences first, and then formulate them correctly.
Response elements:
1) 2 - One of the cells of the pollen grain forms a long pollen tube along which male gametes - sperm cells move
2) 4 - The embryo sac contains the egg and the central nucleus.
3) 5 - One of the sperm fuses with the egg, and the second sperm with the central nucleus.
59. What are the consequences of applying an excess of mineral fertilizers to the soil?
To pollution the environment.
60. Why is the soil in forest plantations populated with mycorrhizal fungi?
Trees enter into symbiosis with fungi, which is why the plants take root well, they can more easily tolerate unfavorable conditions, especially drought, because plant roots receive additional nutrition.
61. What is the function of chlorophyll in a plant cell?
Absorbs the energy of sunlight and converts it into chemical bonds of organic substances.
62. For what purpose is the root tip pinched when transplanting cabbage seedlings?
When the division zone and the growth zone of the main root are removed, cell division and growth at the tips of the lateral roots is activated. Due to the growth of lateral roots, the surface area for absorption of nutrients increases.
Answer: To increase the number of lateral roots, which leads to an increase in the area of plant nutrition.
63. Why is it necessary to loosen the soil when growing plants?
Answer: To improve root respiration and reduce the evaporation of water from the soil.
64. Mosses are representatives of the plant kingdom. The answer should reflect the role of plants in nature and the specific role of mosses associated with their ability to accumulate water and form peat deposits.
Answer:
1) in the process of photosynthesis, they form organic matter and release oxygen into the atmosphere;
2) accumulate and retain water, cause waterlogging of the soil;
3) promote the formation of peat;
4) are producers in the ecosystem and a link in the food chain.
65. Experienced gardeners apply fertilizers to the soil along the edges of the near-trunk circles of fruit trees, and do not distribute them evenly. Explain why?
66. What is the basic rule to follow when collecting mushrooms to maintain their numbers?
The mycelium should not be damaged, since new fruiting bodies will not grow on the destroyed mycelium.
67. How do substances move in multicellular algae in the absence of a conducting system?
Substances dissolved in water move from cell to cell through pores in the membrane and through the membrane by osmosis
1) Treatment of seeds before sowing with pesticides.
2) Application of crop rotation.
3) Sowing of varieties of plants resistant to smut fungi.
69. What are the features of the structure and life of fungi?
1) Fungi are unicellular and multicellular organisms, the body of which consists of thin filaments - hyphae.
3) Reproduction of fungi: by spores, parts of mycelium - vegetative propagation; budding in yeast; sexual reproduction some mushrooms
70. Why does plowing the soil improve the living conditions of cultivated plants?
Answer:
1) promotes the destruction of weeds and weakens competition with cultivated plants;
2) contributes to the supply of plants with water and minerals;
3) increases the supply of oxygen to the roots.
71. What are the characteristics of bryophytes?
Answer:
2) mosses reproduce both sexually and asexually with alternating generations: sexual (gametophyte) and asexual (sporophyte);
3) an adult moss plant is a sexual generation (gametophyte) and a capsule with spores is asexual (sporophyte);
4) fertilization occurs in the presence of water.
72 In the leaves of plants, the process of photosynthesis proceeds intensively. Does it occur in ripe and unripe fruits? Explain the answer.
Answer:
1) photosynthesis occurs in immature fruits (while they are green), since they contain chloroplasts;
2) as they mature, chloroplasts turn into chromoplasts, in which photosynthesis does not occur.
73. Red algae (crimson) live at great depths. Despite this, photosynthesis takes place in their cells. Explain how photosynthesis occurs if the water column absorbs the rays of the red-orange part of the spectrum.
Answer:
1) for photosynthesis, rays are needed not only in the red, but also in the blue part of the spectrum;
2) red pigment is contained in the crimson cells, which absorbs the rays of the blue part of the spectrum, their energy is used in the process of photosynthesis.
74. What is the fruit? What is its significance in the life of plants and animals?
Answer:
1) the fruit is the generative organ of angiosperms;
2) contains seeds, with the help of which there is a reproduction and dispersal of plants;
3) the fruits of plants are food for animals.
75. Prove that the rhizome of a plant is a modified shoot.
Answer:
1) the rhizome has nodes in which there are rudimentary leaves and buds;
2) at the top of the rhizome there is an apical bud, which determines the growth of the shoot;
3) adventitious roots extend from the rhizome;
4) the internal anatomical structure of the rhizome is similar to the stem.
76. What part of the sheet is indicated in the figure with the letter A and what structures does it consist of? What functions do these structures perform?
1) the letter A denotes a vascular-fibrous bundle (vein), the bundle includes vessels, sieve tubes, mechanical tissue;
2) the vessels provide the transport of water to the leaves;
3) sieve tubes provide transport of organic matter from leaves to other organs;
4) cells of mechanical tissue give strength and are the skeleton of the leaf.
77. What are the characteristic features of the mushroom kingdom?
Answer:
1) the body of the mushrooms consists of filaments - hyphae, which form the mycelium;
2) reproduce sexually and asexually (by spores, mycelium, budding);
3) grow throughout life;
4) in the cell: the membrane contains a chitin-like substance, a reserve nutrient - glycogen.
78. Experienced gardeners apply fertilizer to the grooves located along the edges of the near-trunk circles of fruit trees, rather than distributing them evenly. Explain why.
Answer:
1) the root system grows, the suction zone moves behind the apex of the root;
2) roots with a developed suction zone - root hairs - are located at the edges of the trunk circles.
79. What modified shoot is shown in the figure? Name the structural elements indicated in the figure by the numbers 1, 2, 3, and the functions they perform. Sectional drawing of the bulb.
Answer:
1) onion;
2) 1 - a juicy scaly leaf, in which nutrients and water are stored;
3) 2 - adventitious roots, ensuring the absorption of water and minerals;
4) 3 - bud, ensures the growth of the shoot.
80. What are the features of the structure and life of mosses? List at least three items.
Answer:
1) most mosses are leafy plants, some of them have rhizoids;
2) mosses have a poorly developed conducting system;
3) mosses reproduce both sexually and asexually, with alternating generations: sexual (gametophyte) and asexual (sporophyte); the adult moss plant is the sexual generation, and the spore pod is asexual.
81. Why are mushrooms isolated in a special kingdom of the organic world?
Answer:
1) the body of the fungi consists of thin branching filaments - hyphae, which form the mycelium, or mycelium;
2) mycelium cells store carbohydrates in the form of glycogen;
3) fungi cannot be classified as plants, since there is no chlorophyll and chloroplasts in their cells; the wall contains chitin;
4) mushrooms cannot be attributed to animals, since they absorb nutrients from the entire surface of the body, and do not swallow them in the form of food lumps.
82. What are the main signs of the structure and activity of bacteria. Indicate at least four features.
Answer:
1) bacteria - pre-nuclear organisms that do not have a formed nucleus and many organelles;
2) by the way of feeding bacteria - heterotrophs and autotrophs;
3) high reproduction rate by division;
4) anaerobes and aerobes;
5) unfavorable conditions are experienced in a state of dispute.
83. What are the features of the structure and life of fungi? Indicate at least three signs.
Answer:
1) mushrooms - unicellular and multicellular organisms, the body of which consists of thin filaments - hyphae;
3) reproduction of fungi: by spores, parts of mycelium - vegetative reproduction; budding in yeast; sexual reproduction of some fungi.
84. What is the complication of ferns in comparison with mosses? Give at least three signs.
Answer:
1) ferns have roots;
2) in ferns, in contrast to mosses, a developed conductive tissue has formed;
3) in the fern development cycle, the asexual generation (sporophyte) prevails over the sexual one (gametophyte), which is represented by an outgrowth.
85. What are the characteristics of plants living in arid conditions?
Answer:
1) the root system of plants penetrates deeply into the soil, reaches the groundwater or is located in the surface layer of the soil;
2) in some plants, water during a drought is stored in leaves, stems and other organs;
3) the leaves are covered with a waxy coating, pubescent or modified into spines or needles.
86. Name at least three aromorphoses in land plants that allowed them to be the first to master the land. Justify the answer.
Answer:
1) the emergence of integumentary tissue - the epidermis with stomata - contributing to protection against evaporation;
2) the emergence of a conducting system that ensures the transport of substances;
3) the development of mechanical tissue that performs a supporting function.
87. What are the features of the structure and life of cap mushrooms? Name at least four features.
Answer:
1) have mycelium and fruiting body;
2) reproduce by spores and mycelium;
3) by the way of feeding - heterotrophs;
4) most form mycorrhiza.
88. In what ways does the kingdom of mushrooms differ from the kingdom of plants? Name at least three signs.
Answer:
1) fungi are heterotrophs, not capable of photosynthesis;
2) mushrooms differ in structure and chemical composition cells: do not have chloroplasts, the cell wall contains chitin, the reserve nutrient is glycogen;
3) the body of the mushrooms is formed by hyphae.
89. Can the seeds in the garden grow with their roots up, and down with shoots, if they were sown at random?
1. No
2. The root grows vertically downward (geotropism), and the shoot grows upward (phototropism).
90. Why are large seeds selected for sowing?
1. Large seeds contain more nutrients.
2. Larger seeds produce stronger shoots.
91. Why does plowing the soil improve the living conditions of cultivated plants?
1. Promotes weed control and reduces crop competition.
2. Promotes the supply of plants with water and minerals.
3. Increases the supply of oxygen to the roots.
92. What fertilizers and why is it necessary to apply to the soil to get a large head of cabbage?
1. Nitrogen (urea, potassium nitrate, ammonium sulfate)
2. Because they enhance the growth of stems and leaves.
93. What fertilizers and why is it necessary to apply to the soil in order to get large tubers from potatoes?
1.potassium fertilizers (potassium chloride, potassium nitrate)
2.because they enhance the growth of roots, bulbs and tubers
94. What fertilizers and why is it necessary to apply to the soil in order to get large fruits of tomatoes?
1. Phosphate fertilizers (superphosphate, bone meal)
2. since they accelerate the growth and ripening of fruits.
95. What is the difference between the embryos of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants?
1.In dicots, the embryo usually has 2 cotyledons, in monocots
2. In dyad-x the embryo is symmetrical, and in one-x - asymmetric.
3. In dicots, cotyledons usually germinate aboveground, in monocots, usually underground.
96. What tissue of flowering plants connects its organs into a single whole?
Conductive tissue (vessels of wood and sieve tubes of bast)
97. What is the difference between plants and animals? Name at least three signs.
1) plants lead an attached lifestyle and grow throughout life;
2) plant cells contain plastids, chlorophyll, cellulose cell walls, vacuoles with cell sap;
3) plants - autotrophs, producers, capable of creating organic substances from inorganic ones using solar energy and emitting oxygen.
98. What are the characteristics of the plant kingdom?
1) the presence of chloroplasts in cells, in which photosynthesis occurs
2) the presence in the cells of a membrane of fiber and vacuoles with cell sap
3) grow throughout life, most do not mix from one place to another
99. What are the features of the structure and life of mosses?
1) most mosses are leafy plants, some of them have rhizoids
2) mosses have a poorly developed conducting system ";"
3) mosses reproduce both sexually and asexually, with alternating generations: sexual (gametophyte) and asexual (sporophyte); an adult moss plant is a sexual generation, and a capsule with spores is asexual
100. What are the characteristics of conifers?
1.propagation by seeds that lie open on the scales of the cones
2.No aquatic environment for fertilization
3.leaves are scaly or needle-like, covered with a waxy bloom
101. What are the characteristics of angiosperms?
1.the presence of a flower
2.the presence of fruits with seeds
3. double fertilization
4.diversity of ecological forms and groups
102. What processes ensure the movement of water and minerals in the plant? Explain the answer.
1) from the root to the leaves, water and minerals move through the vessels due to transpiration, as a result of which sucking force arises;
2) the upward current in the plant is facilitated by the root pressure, which arises as a result of the constant flow of water into the root due to the difference in the concentration of substances in the cells and the environment.
103. What process in the life of a tree is disturbed when its bark is removed?
Without the bark and sieve tubes in it, the plant will not be able to conduct organic matter to the cells of the roots and other organs and will soon die.
104. Growth rings are visible on the tree cut. Explain why they have different widths.
The tree-ring width depends on the environmental conditions, which changed in different years of the tree's life; under favorable conditions, the width of the ring is greater, since the cambium is divided more intensively.
106. Prove that the rhizome of a plant is a modified shoot.
1. The rhizome has nodes containing rudimentary leaves and buds; apical bud, determines the growth of the shoot.
2. The adventitious roots extend from the rhizome; the internal anatomical rhizome is similar to the stem.
107. Determine which part of the onion bulb is indicated in the figure with the letter B, explain its structure and functions.
1) a modified sheet;
2) structure: juicy white scales, devoid of chlorophyll, have a thin skin;
3) functions: a supply of water with nutrients dissolved in it.
108. What functions do the leaves of the plant perform in addition to air nutrition?
Sheet functions:
1. Breathing (gas exchange) - the absorption of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide, occurs through the stomata of the leaf.
2. Transpiration - evaporation of water by leaves. Excess water in the form of water vapor is evaporated by leaves through the stomata. The evaporation of water protects the plants from overheating.
3. The leaf protects plants from slagging, in the form of autumn leaf fall. Together with the fallen leaves, the plant is freed from unnecessary and harmful substances.
4. Leaf is an organ of vegetative reproduction.
109. What is the role of stomata in the life of a plant?
110. Plants are predators, such as sundew, feed on small insects. Explain what is the reason for this way of eating?
This is due to the fact that the sundew plant grows in a swamp, and the soil in a swamp is very poor in humus, so the plant receives little mineral salts, including those containing nitrogen. Nitrogen salts are needed for the formation of proteins in the body. Dewdrop, "digesting" animal proteins, thus overcomes protein hunger. Such nutrition is associated with the habitat and arose as an adaptation to environmental conditions.
111. How can you explain that multicellular plants consist of several types of tissues?
With the advent of multicellularity, various functions appeared in plant organs, and these functions could only be performed by special formations - tissues. To organs that are far from each other, it is necessary to conduct substances, this is done by conductive tissues. Excess substances accumulate in the cells of the underlying tissue, etc.
112. Why did angiosperms occupy a dominant position on Earth?
1. The life forms of angiosperms are represented by trees, shrubs, grasses, which determines their greatest ecological plasticity.
2. Vegetative organs (roots, leaves, shoots) have numerous modifications and are the most specialized in structure and function.
3. Seeds of angiosperms are protected by the pericarp, which contributes to their better preservation and distribution.
4. Fertilization does not require water, and pollination methods are very diverse (insects, wind, self-pollination, etc.).
5. They are spread by wind, water, animals or humans.
113. Why do many seeds not germinate when there is an excess of water in the soil?
114. The seeds of the Siberian pine are called pine nuts. Explain. Is this name scientifically fair?
1) nut - the fruit of angiosperms;
115. Why without plants life in modern form on Earth would be impossible?
1) plants in the process of photosynthesis form organic matter - food for other organisms;
2) they maintain a constant gas composition of the atmosphere, emitting oxygen in the light and absorbing carbon dioxide.
116. How is the complexity of ferns manifested in comparison with mosses? Give at least 3 signs.
117. Red algae live at great depths. Despite this, photosynthesis takes place in their cells. Explain how photosynthesis occurs. If the water column absorbs the rays of the red-orange part of the spectrum.
1) the rays of the red and blue parts of the spectrum are needed for photosynthesis;
2) red pigment is contained in the crimson cells, which absorbs the rays of the blue part of the spectrum, their energy is used in the process of photosynthesis.
118. What are the fruits indicated letters A, B, and the plants for which they are characteristic. What do their fruits have in common? What is the difference?
1) A-caryopsis (wheat). B - achene (sunflower);
2) general: dry single-seeded fruits;
3) differences: in the caryopsis, the seed coat has grown together with the pericarp, the unopening fruit, the achene is the unfolding fruit.
119. Which kidney is shown in the picture? What elements of its structure are designated by numbers 1 and 2? What tissue is responsible for the development of the kidney?
1) flower (generative) bud;
2) 1 - rudimentary stem, 2 - rudimentary flower (inflorescence);
3) the growth and development of the kidney is due to the educational tissue in the growth cone
120. How do dicotyledonous plants differ from monocotyledonous plants? Give at least 4 signs.
1) in dicotyledons there are two cotyledons in the embryo of the seed, in monocotyledons - one;
2) the root system of dicots is, as a rule, pivotal, and monocots are fibrous;
3) in dicotyledons, the leaves are simple and complex, the venation is reticulate, in monocotyledons the leaves are always simple, the venation is parallel and arched;
4) as a rule, in dicotyledonous flowers with a double perianth, four- or five-membered, in monocots - flowers with a simple perianth, three-membered.
121. What functions do different zones of a young root perform?
1. In the division zone, the number of young cells increases, the growth of the root in length;
2. In the growth zone, the cells increase in size and their differentiation occurs;
3. In the suction zone, root hairs absorb water with dissolved minerals from the soil;
4. The movement of substances is carried out in the area of movement.
122. How is the work of stomata regulated?
1. the gap is located in the epidermis, surrounded by two guard cells and serves for transpiration and gas exchange.
2. guard cells are involved in photosynthesis and the accumulation of organic matter;
3. With the accumulation of carbohydrates, water enters the guard cells. The turgor pressure increases, the stomatal gap opens in the absence of photosynthesis, the guard cells collapse, the gap closes.
123. What is the difference between a pine seed and a fern spore? Their similarities.
1. The seed, in contrast to the unicellular spore, is a multicellular formation, consists of an embryo and accumulated substances
2. The spore has a haploid set of chromosomes, giving rise to a gametophyte. The embryo of the seed is diploid, giving rise to a sporophyte, an adult plant
3.seed as a spore ensures the propagation and spread of plants
124. Explain, due to what the water rises along the trunks of trees for tens of meters, for example, near eucalyptus - up to 100 m. Answer:
1) under the influence of root pressure;
2) due to the evaporation of water from the surface of the leaves.
125. All plants are conventionally divided into lower and higher. Along with the similarities, there are also differences between them. What is the most important of them?
In the body of lower plants (thallus, thallus) there are no tissues and organs.
126. Mossy - one of the most ancient groups of plants. From whom did they originate in the process of evolution? How can this be proven?
Mossy in the process of evolution evolved from algae. This is confirmed by the great similarity of the protonema (pregrowth) of mosses with filamentous green algae.
127. Bryophytes are the second largest division of higher plants after angiosperms. They are widespread across the globe. What is their main importance in nature?
1) Cause waterlogging of the area.
2) Participate in the formation of peat.
3) Can participate in soil formation.
128. One of the prerequisites for the successful emergence of plants on land was the acquisition of tissues specialized in carrying various substances through the body. In the course of evolution, the importance of these tissues has expanded. List the functions that conductive tissues can perform in modern vascular plants?
1) Conduct nutrients.
2) Serve as the main support for plants
3) Participate in the storage of nutrients.
129. It is known that in agricultural practice, before sowing seeds, they are checked for germination. Explain how and why this is done.
1) to determine the germination of seeds, a certain number of them (100) are placed in optimal conditions for germination and the percentage of germinated seeds is calculated;
2) germination is determined to establish the quality of the seed, on which the yield of the plant depends.
130. Why are mosses classified as the highest spore plants?
1.differentiation of cells occurred, tissues appeared
2.the body is divided into organs: stem and leaves
3.produce by spores
131. In what forms are movements manifested in plants? Answer:
1.bends of plants towards the light - phototropism
2.movement of the stem upward, and the root downward under the influence of gravity - geotropism
3. movement of plants under the influence of chemicals or mechanical influences - chemotropism.
132. Woody plants growing in areas with a constant wind direction have a flag-shaped crown. Plants grown from cuttings of these trees under normal conditions have a normal crown shape. Explain these phenomena.
1) the flag-shaped crown is formed under the influence external conditions(wind) and is explained by modification variability;
2) during vegetative propagation with the help of cuttings, the genotype does not change; in the absence of wind, a normal crown is formed.
133. What type of sheet is shown in the picture? Which parts of the sheet are indicated in the figure with numbers 1 and 2 and what functions do they perform?
1) a simple leaf with reticulated veins and stipules;
2) 1 - leaf blade, performs the functions of photosynthesis, gas exchange, transpiration, in some plants, vegetative reproduction;
3) 2-veins provide transport of substances, support of the leaf.
134. Name the parts of the flower indicated on the diagram by the numbers 1, 2, 3, and explain their functions.
1) 1- stamens - an organ of sexual reproduction, form pollen, which takes part in pollination;
2) 2 - pistil ovary, participates in sexual reproduction, contains an ovule with an ovum (female gamete);
3) 3 - sepals and corolla petals (perianth), serve to protect the stamens and pistil, participate in attracting insects (pollination).
135. Name the parts of the woody stem, indicated in the figure by the numbers 1, 2, 3, and indicate the functions that they perform.
1) 1- cork (integumentary tissue), performs a protective function;
2) 2 - bast (bast fibers and sieve tubes), performs a mechanical function and conducts organic substances;
3) 3 - cambium (educational tissue), ensures the growth of the tree in thickness.
136. Name the vegetative organ of the plant shown in the figure, its structures, indicated by numbers 1 and 2, and the functions they perform. What role does this vegetative organ play in plant life?
1) bulb - a shortened modified shoot, participates in vegetative reproduction, accumulates nutrients;
2) 1 - the bottom, a modified stem, from which the adventitious roots grow and buds are formed on it;
3) 2 - dry scaly leaf; protects the bulb from drying out and damage.
137. On what grounds are plants of the Liliaceae and Cereals families classified as Monocotyledonous? Indicate at least 4 signs.
1) a seed with one cotyledon;
2) fibrous root system;
3) simple leaves with parallel or arcuate venation;
4) a three-membered flower with a simple perianth.
138. What parts of the bean seed embryo are indicated in the figure by numbers 1 and 2, what functions do they perform?
1) 1 - root, bud (embryonic stem and leaves), 2 - cotyledons;
2) the root develops into the main root, the shoot develops from the bud;
3) cotyledons - provide the seedling with nutrients.
139. In small rooms with an abundance of indoor plants, the oxygen concentration decreases at night. Explain why.
1) at night, with the cessation of photosynthesis, the release of oxygen stops;
2) in the process of respiration of plants (they breathe constantly), the concentration of oxygen decreases and the concentration of carbon dioxide increases.
140. The corn plant has two types of inflorescences: the ear and the panicle. Why are fruits formed only on the cob and sometimes part of the cob is not filled with grains?
1) the ear consists of female flowers, in which fruits are formed - weevils, the panicle consists of male flowers;
2) not all flowers of the cob are pollinated and fertilized, so part of the cob will be empty.
141. It is known that it is difficult to detect the respiration of plants experimentally in the light. Explain why.
1) in the light in the plant, along with respiration, photosynthesis occurs, in which carbon dioxide is used;
2) as a result of photosynthesis, much more oxygen is generated than is used in plant respiration.
142. Determine the zones of the root, indicated in the figure by the numbers 1,2,4, and indicate their functions.
Response elements:
1) 1- root cap, protects the root tip from mechanical damage;
2) 2 - division zone, provides root growth in length due to cell division;
3) 4 - the zone of suction, the zone of root hairs, ensures the absorption of water and minerals.
143. Why does the growth of the root stop in length after removing its apex? What is the purpose of this technique when transplanting plants?
1) educational tissue is located at the apex of the root, the removal of which leads to the cessation of root growth in length
2) removal of the root apex promotes the formation of lateral roots, which increase the plant's nutritional area.
144. Plants consume a significant amount of thieves during their life. What are the two main life processes that consume most of the water consumed? Explain the answer. Answer elements:
1) evaporation, ensuring the movement of water and solutes and protection from overheating;
2) photosynthesis, during which organic matter is formed and oxygen is released.
145. Why potato tubers are not classified as fruits. Explain the answer. Give at least 3 pieces of evidence. Response elements:
1) tubers do not have seeds;
2) their formation and development is not associated with the structures of the flower;
3) the structure of the tuber corresponds to the modified shoot
146. What is the difference between a pine seed and a fern spore and what is their similarity?
1) the seed, in contrast to the unicellular spore, is a multicellular formation, consisting of an embryo and a supply of nutrients;
2) the spore has a haploid set of chromosomes and gives rise to a gametophyte (an outgrowth), and the embryo of a seed is diploid and gives rise to a sporophyte (an adult plant);
3) the seed, like the spore, ensures the reproduction and dispersal of plants.
147. Explain why nitrogen fertilization is not required to grow legumes.
1) root nodule bacteria settle on the roots of legumes;
2) they assimilate nitrogen from the air and provide plants with nitrogen nutrition.
148. What part of the sheet is indicated in the figure by the letter A and what structures does it consist of? What functions do these structures perform?
1) the letter A denotes a vascular-fibrous bundle: (vein), the bundle includes vessels, sieve tubes, mechanical tissue;
2) the vessels provide the transport of water to the leaves;
3) sieve tubes provide transport of organic matter from leaves to other organs;
4) cells of mechanical tissue give strength and - are the skeleton of the leaf.
149. Describe the features of the plant kingdom. Give at least four signs.
1) the presence of chloroplasts in the cells, in which photosynthesis occurs;
2) the presence of a strong fiber shell in the cell, which gives it its shape;
3) the presence of vacuoles filled with cell sap;
4) growth throughout life, practically do not move from one place to another;
5) absorption of nutrients by the surface of the body.
150. What is the complication of ferns in comparison with mosses? Give at least three signs.
1) ferns have roots;
2) in ferns, in contrast to mosses, a developed conductive tissue has formed;
3) in the fern development cycle, the asexual generation (sporophyte) prevails over the sexual one (gametophyte), which is represented by an outgrowth.
151. Why is a tuber considered a modified underground shoot? Please provide at least three pieces of evidence.
1) chloroplasts are formed in the light, in which photosynthesis occurs;
2) buds (eyes) are located on the tuber;
3) there are nodes and internodes like the shoot.
152. By what signs will you distinguish a modified shoot from a modified root?
1) The modified root has no buds
2) The modified roots do not have scales - modified leaves.
153. The researcher took two groups of cells and placed them in different tubes with culture medium. He removed the nucleus from one group of cells. Another group of cells remained unharmed. How will the number of cells change in different groups after a while and why?
1) The nucleus is responsible for cell division.
2) Without a nucleus, cells do not divide and die after a while.
154. How can you explain that multicellular plants consist of several types of tissues?
1) the need to absorb and deliver nutrients at different distances in connection with landfall.
2) in connection with the performance of various functions by plant organs.
155. What features of development helped plants to conquer the land?
1) The emergence of organs that perform certain functions.
2) the appearance of specialized tissues.
3) The appearance of flower and seed.
4) Reducing the dependence of the reproduction of the organism on water.
156. The process of photosynthesis is intensively taking place in the leaves of plants. Does it occur in ripe and unripe fruits?
1) photosynthesis occurs in immature fruits (while they are green), since they contain chloroplasts;
2) as they mature, chloroplasts turn into chromoplasts, in which photosynthesis does not occur.
157. It is known that in sphagnum bogs, despite the large amount of moisture, water is inaccessible to many plants. What is the reason for this?
1) the roots, like other plant organs, carry out the process of respiration and need oxygen, in sphagnum bogs, due to poor aeration, it is not enough;
2) acidification of water and soil of bogs also interferes with root growth;
3) and toxic substances accumulate in the water and soil of sphagnum bogs, which interfere with the development of plants.
158. Why do many seeds not germinate when there is an excess of water in the soil?
With an excess of water in the soil, there is a lack of oxygen, which is necessary for the respiration of the plant. Germinating seeds of most plants receive a significant part of the oxygen from the free spaces of the soil, and not from water.
159. It is known that before transplanting young plants into the ground, they are picked (pinched off the tip of the main root). Why do they do this?
1) when picking plants, the growth of adventitious and lateral roots is activated;
2) due to an increase in the total number of adventitious and lateral roots, the mineral nutrition of the plant improves, which stimulates its growth.
160. With the introduction of potatoes into cultivation, potato riots arose in Russia. Why didn't the peasants want to grow this plant?
1) the peasants did not know that it was necessary to eat tubers and ate green berries;
2) potato berries are poisonous and cause severe poisoning.
161. Gardeners, when picking cabbage seedlings, pinch the top of the main root, and when propagating currant bushes, they use stem cuttings, on which adventitious roots develop. Both of these flowering plants belong to the dicotyledonous class. Explain what type of root system will be found in cabbage grown from this seedling, and what type of root system will be in currant grown from stem cuttings.
1) The type of root system initially in cabbage and currant (dicotyledonous plants) tap.
2) When the cabbage is picked, after the pinching, the main root stops growing in length (since the division and growth zones are removed) and the lateral and adventitious roots develop. When rooting stem cuttings of currant, adventitious roots develop. Thus, the root system in both cases will become similar to fibrous (predominant development of lateral and adventitious roots).
162. The flowers of many angiosperms are pollinated by insects. Explain the mutual benefits of cross-pollination for insects and plants.
1) For plants: thanks to insects, the likelihood of pollination increases, the possibility of the offspring acquiring new traits (variability and better adaptability) increases.
2) For insects: plants are a source of food (pollen and nectar), a refuge.
163. Why does plowing the soil improve the living conditions of cultivated plants?
1) promotes the destruction of weeds and weakens competition with cultivated plants;
2) contributes to the supply of plants with water and minerals;
3) increases the supply of oxygen to the roots.
164. In the 17th century, the Dutch scientist Van Helmont conducted an experiment. He planted a small willow in a tub of soil, after weighing the plant and soil, and only watered it for several years. After 5 years, the scientist weighed the plant again. Its weight has increased by 63.7 kg, while the weight of the soil has decreased by only 0.06 kg. Explain, due to what there was an increase in the mass of the plant, what substances from the external environment provided this increase.
1) the mass of the plant has increased due to organic substances formed in the process of photosynthesis;
2) in the process of photosynthesis, water and carbon dioxide are used, which come from the external environment.
165. What is the significance of leaf fall for plants of middle latitudes?
1) Leaf fall is the adaptation of plants to reduce water evaporation in autumn and winter.
2) And the likelihood of breaking off branches under the weight of snow also decreases.
3) In addition, this is how harmful substances accumulated over the summer are removed from the plant.
166. Name the adaptation of plants to life in arid conditions.
1) the root system of plants penetrates deeply into the soil, reaches the groundwater or is located in the surface layer of the soil;
2) in some plants, water during a drought is stored in leaves, stems and other organs;
3) the leaves are covered with a waxy coating, pubescent or modified into spines or needles.
167. What is the significance in the life of plants for beekeepers placing hives on buckwheat fields?
Bees feed on buckwheat pollen and nectar, cross-pollinate, which increases the productivity of plants.
168. If during the flowering of apple trees there is cold rainy weather, then the apple harvest decreases. Explain the reasons.
1) the apple tree is an insect pollinated plant, and insects do not fly in cold rainy weather,
2) pollination, fertilization and fruit formation do not occur.
169. Why does potato yield increase after hilling?
Hilling stimulates the formation of adventitious roots, which means that it increases the mass of the root system. As a result, root nutrition is improved and the yield of potatoes is increased.
170. Why is it necessary to loosen the soil when growing plants?
Loose soil contains more oxygen required for plant respiration. In addition, during loosening, soil capillaries are disturbed, through which water easily rises to the surface and then evaporates. Thus, moisture is retained in the soil (which is why loosening is often called dry irrigation).
171. Experienced gardeners apply fertilizers to the soil along the edges of the near-trunk circles of fruit trees, and do not distribute them evenly. Explain why?
The root system grows, the suction zone moves behind the root apex. Roots with a developed zone of suction - root hairs - are located at the edges of the trunk circles.
172. How, using a magnet, you can cleanse seeds of cultivated plants (for example, flax, clover, alfalfa) from weed seeds?
1) weeds have fuzzy seeds that cling to animal hair
2) the contaminated seeds are sprinkled with iron powder (grains of iron stick around the weed seeds), and then, using a magnet, they are divided into clean seeds and weed admixture
173. What is the significance of photosynthesis for life on Earth?
The importance of the process of photosynthesis for life on Earth is as follows: photosynthesis provides all living organisms with the organic substances they need. During photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy available to living organisms. In the light phase of photosynthesis, a by-product is released - molecular oxygen, which is necessary for respiration by most organisms.
174. What processes ensure the movement of water and minerals in the plant? Explain the answer.
1) from the root to the leaves, water and mineral salts dissolved in it move through the vessels due to transpiration, as a result of which sucking force arises;
2) the upward flow of the plant is facilitated by the root pressure, which arises as a result of the constant flow of water into the root due to the difference in the concentration of substances in the cells and the environment.
175. Explain through which tissues and how the transport of substances is carried out in angiosperms.
1) the movement of water and minerals is carried out through the vessels of wood;
2) the movement of organic substances occurs along the sieve tubes of the bast;
3) water and minerals move from the roots along the stem to the leaves as a result of root pressure and sucking force arising from the evaporation of water;
4) organic substances move from photosynthetic cells due to the difference in concentration and pressure.
176. Find errors in the text given, correct them, indicate the numbers of the sentences in which they are made, write down these sentences without errors.
1. Plants, like all organisms, have a metabolism.
2. They breathe, feed, grow and reproduce.
3. When breathing, they absorb carbon dioxide and give off oxygen.
4. They grow only in the first years of life.
5. All plants are autotrophic organisms by the type of nutrition, they multiply and spread with the help of seeds.
Response elements:
1) 3- when breathing, plants absorb oxygen and emit carbon dioxide;
2) 4 - plants grow throughout their life;
3) 5 - not all plants form seeds
177. What is called double fertilization?
In flowering plants, in addition to the fusion of haploid gametes - one of the sperm with the egg and the formation of a diploid zygote, from which the seed embryo develops, the second sperm fusion with the diploid secondary cell and the formation of triploid cells, from which the endosperm is formed.
178. In what processes of life of plants does water participate?
Water participates in root nutrition, the movement of substances inside the plant, photosynthesis and evaporation, cooling the surface of the leaves and protecting them from burns.
179. Read the text "Fertilization in flowering plants" and find sentences in it that contain biological errors. Write down the numbers of these sentences first, and then formulate them correctly.
1. A grain of pollen, once on the stigma of the pistil, germinates. 2. One of the cells of the pollen grain forms a long pollen tube, along which female gametes - eggs - move. 3.Longering, the tube passes between the cells of the stigma, the column and reaches the ovule. 4. The embryo sac contains two mature sperm. 5. One of the sperm fuses with the egg, and the second dies. 6. The fusion of female and male gametes is called fertilization.
1) 2 - One of the cells of the pollen grain forms a long pollen tube along which male gametes - sperm cells move
2) 4 - The embryo sac contains the egg and the central nucleus.
3) 5 - One of the sperm fuses with the egg, and the second sperm with the central nucleus.
180. What role do stomata play in plant life?
The stomata is a highly specialized formation of the plant epidermis, consisting of two guard cells and an intercellular space (stomatal gap) between them. Transpiration and gas exchange are carried out through the stomata. Transpiration is the evaporation of water by a plant. Transpiration regulates the water and temperature conditions of the plant.
181. What is the difference between root crops and root tubers?
The root crop is formed from the main root and the lower part of the stem, root tubers - from the lateral and adventitious roots.
182. Prove that the lily of the valley rhizome is a modified shoot.
1) the rhizome has nodes in which there are rudimentary leaves and buds;
2) at the top of the rhizome there is an apical bud, which determines the growth of the shoot;
3) adventitious roots extend from the rhizome;
4) the internal anatomical structure of the rhizome is similar to the stem.
183. What biological characteristics of cabbage should be taken into account when growing it?
ANSWER: Its cold resistance, moisture-loving, photophilous, requirements for the nutritional value of the soil and the fact that it is a biennial plant.
184. Why are there no plants or are very thinned out on forest paths?
ANSWER: Constant trampling leads to soil compaction, disruption of the water and air regime of the roots, and oppression of plants.
185. Why do apples of many varieties become loose after long storage?
ANSWER: During long-term storage, the intercellular substance is destroyed.
186. In the wetlands of the tundra, many plants suffer from a lack of moisture. What is the reason for this?
ANSWER: Cold water poorly absorbed by the roots.
187. What is the manifestation of the adaptability of plants to life in the tundra?
1. There is a lot of light in the tundra in summer, but there is a lack of temperature, and therefore the soil thaws to a shallow depth, under which there is permafrost.
2. the roots cannot go into the soil, which means there are no tall plants in the tundra, the vegetation cover is represented by lichens, mosses, herbaceous plants
3.Trees such as dwarf birch and willow are represented by dwarf forms
4.in the tundra - short growing season, small leaves
188. Why, when storing potato tubers, does their mass decrease by spring?
ANSWER: During storage, living cells breathe and during respiration use organic matter and evaporate water
189. Why do potato tubers become crumbly after long cooking?
ANSWER: During cooking, the intercellular substance that binds cells is destroyed.
190. Why is sweetish juice released when frozen apples are thawed?
ANSWER: When frozen, cells are destroyed, and when thawed, cell juice flows out of the vacuoles.
191. Why does the cut surface become wet when an apple is cut?
ANSWER: When cut, vacuoles are damaged, and cell juice flows out of them.
192. What features of psilophytes allowed them to be the first to master the land? Justify the answer.
ANSWER: The appearance of integumentary tissue - the epidermis with stomata to protect against evaporation. The emergence of an underdeveloped conducting system for the transport of substances. The emergence of mechanical tissue to perform the supporting function. The presence of rhizoids for anchoring in the soil.
193. What are the similarities and differences between the fruits of plants of the family Moths (Legumes) and Crucifers (Cabbage)?
ANSWER: Moths have a bean fruit, and Crucifers have a pod or pod. Similarities: bean and pod (pod) - dry polyspermous opening fruits. Differences: the seeds inside the bean lie on the valves, and in the pod, on the membranous septum.
194. What are the similarities and differences between the fruits of plants of the Cereals and Asteraceae families?
ANSWER: Similarities: they have one-seeded, non-opening fruits. Differences: in cereals, the fruit is a caryopsis, and in Compositae, an achene. In the caryopsis, the seed coat grows together with the pericarp, and in the achene, the seed lies freely, the fruits may have crests, parachutes, attachments.
195. The student in his answer indicated that plants of the Moth family (Legumes) have a regular five-membered flower, a fibrous root system and a fruit pod. Find errors in this answer and comment on them.
ANSWER: The flower of the Moths is five-membered, irregular: an unpaired petal - a sail, paired ones - oars and fused ones - a boat. The root system is pivotal, since this family belongs to the class of Dicotyledons. The fruit is a bean, not a pod.
196. Explain why, when sowing small seeds to a great depth, seedlings do not develop?
ANSWER: Small seeds contain few nutrients, which are not enough for the seedling to reach the soil surface.
197. What features of the drupe fruit ensure the spread of seeds of many representatives of plants of the Rosaceae family?
ANSWER: Drupe is a single-seeded fruit with brightly colored juicy pulp, which attracts animals. Drupes are eaten by birds and mammals, while the seeds, covered with the lignified part of the pericarp, are not digested in the alimentary canal and are removed with droppings outside.
198. What is the significance of various flowers in the inflorescences of plants of the Asteraceae family?
ANSWER: tubular and reed-for the formation of seeds (located in the center), funnel-shaped and pseudo-lingual - to attract pollinating insects (located at the edges).
199. Name at least 3 features of land plants that allowed them to be the first to master the land. Justify the answer.
ANSWER: 1) the emergence of integumentary tissue - the epidermis with stomata, which helps to protect against evaporation; 2) the emergence of a poorly developed conducting system that ensures the transport of substances; 3) the development of mechanical tissue that performs a supporting function; 4) the formation of rhizoids, with the help of which they were fixed in the soil.
200. What is the relationship between the evaporation of water and the movement of minerals in the plant?
1) As a result of the evaporation of water by leaves, its content in plant cells decreases, and the concentration of cell sap increases, and the osmotic pressure increases;
2) Due to osmotic pressure, water with salts dissolved in it flows from the root and stem to the leaves.
1) In a saline solution, cells lose water, plasmolysis occurs;
2) The cells shrink, the turgor falls, the plant withers.
201. What are the structure and functions of seeds in flowering plants?
1) Structure: peel, embryo, endosperm (sometimes underdeveloped)
2) Seeds provide plant propagation
3) Provide relocation and transfer of adverse conditions
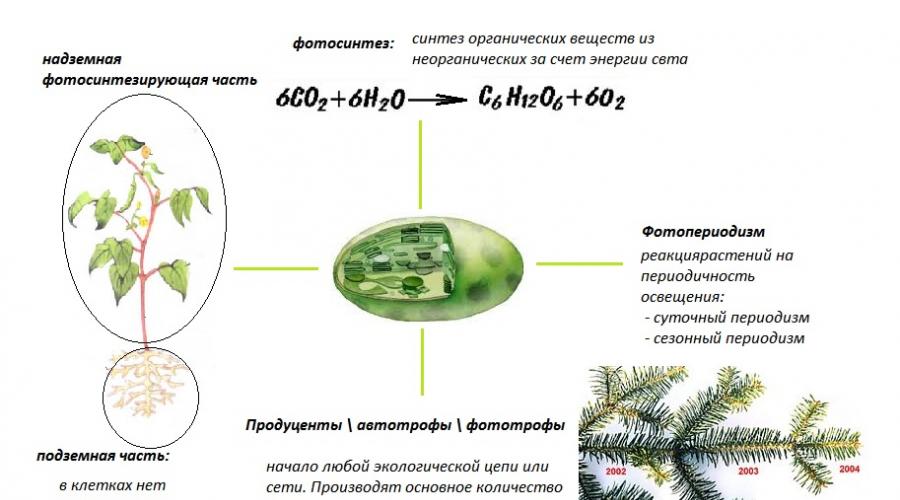
Botany- a science that studies the plant kingdom (Greek. botane- grass, plant).
The ancient Greek scientist Theophrastus (III century BC), a student of Aristotle, created a system of botanical concepts, systematizing and generalizing all the knowledge of farmers and healers known at that time with his theoretical conclusions. It is Theophrastus who is considered the father of botany.
Modern botany- the science of morphology, anatomy, physiology, ecology and taxonomy of plants
Signs of the Plant Kingdom
- eukaryotes;
- autotrophs (the process of photosynthesis);
- osmotrophic type of nutrition: the ability of cells to absorb only low molecular weight substances;
- unlimited growth;
- motionless lifestyle;
- reserve substance - starch (accumulates in plastids during photosynthesis);
Features of the structure of a plant cell (Fig. 1):
- cellulose cell wall
The presence of a cell wall prevents food particles and large molecules from entering the cell; therefore, plant cells absorb only low molecular weight substances (osmotrophic type of nutrition). Plants absorb water and carbon dioxide from the environment, for which the cell membrane is permeable, as well as mineral salts, for which channels and carriers exist in the cell membrane. - plastids (chloroplasts, chromoplasts, leukoplasts);
- large central vacuole
A bladder with cell sap, surrounded by a membrane - tonoplast. The tonoplast has a system of regulated carriers that transfer various substances to the vacuole, maintaining the desired salt concentration and acidity in the cytoplasm. In addition, the vacuole provides the required osmotic pressure in the cell, which leads to the appearance turgor- stress on the cell wall, which maintains the shape of the plant. The vacuole also serves as a place for storing nutrients and accumulating metabolic waste. - there are no centrioles in the cell centers of plants.
Rice. 1. Plant cell
plant classification
The main ranks of plant taxa are distributed according to the principle of hierarchy(subordination): larger taxa combine smaller ones.

For example:
Plant kingdom
Department of Angiosperms
class Dicotyledonous
family Asteraceae
genus Chamomile
kind Chamomile pharmacy

Life form- the appearance of the plant.
Basic life forms: tree, shrub, shrub and grass.
Wood- a perennial plant with a large lignified trunk.
Bush- a plant with numerous medium-sized lignified trunks that live no more than 10 years.
Shrub- a low-growing perennial plant with lignified trunks, up to 40 cm high.
Herbs- herbaceous green shoots that die off every year. In biennial and perennial grasses, new shoots grow from wintering buds in spring.
higher and lower plants
Different groups of plants differ significantly in structure.
Lower plants have no organs and tissues. Their body is thallus, or thallus... The lower plants include algae. Most of them live in the aquatic environment. Under these conditions, they receive nutrition by absorbing substances throughout the body surface. All or most of the cells of these plants are exposed to light and are capable of photosynthesis. Therefore, they do not need to quickly move substances through the body. The cells of these plants in most cases have the same structure.
Other photosynthetic organisms are also found in the aquatic environment. These are primarily cyanobacteria, which are sometimes called blue-green algae. These are prokaryotic organisms that are not plants.
Higher plants that live in water are often called algae. In these cases, the term "algae" is used in an ecological rather than a systematic sense.
Higher plants have functionally different organs formed by specialized cells. Basically, they live on land. They receive water and mineral nutrition from the soil, and in order to carry out photosynthesis they must rise above its surface, therefore, for such plants it is necessary to move substances between parts of the body (conductive tissue) and mechanical support and support for the ground-air environment (mechanical and integumentary tissues).
The presence of specialized cells, tissues and organs allowed them to reach large sizes and master a wide range of habitats. Many representatives of higher plants returned to the water for the second time. In fresh water bodies, they constitute the bulk of aquatic vegetation.