What refers to building materials. II. Natural stone materials. I. Mineral binders
Classification:
Natural
Artificial
By phase state:
On the use of PGS (industrial civil engineering):
Construction of buildings and structures
For road construction
For the construction of fences of rivers and water bodies
For the construction of special constructions (factories, plants with special
requirements of materials).
Construction products of widespread consumption:
For building structures (foundation materials, wall, roofing,
glazing materials, materials for internal and exterior trim).
Natural: wood, stone.
Overhead (granites, swop, Gneisi)
Metamorphic (marble, talanit, tanker, crushed stone natural)
Sedimentary breeds (sands, clay, sandstone)
The most durable: granites, marbles, gneisses, swop.
The most fragile from the erupted: PEMZA.
The method of destruction of arrays by an explosion with subsequent sawing (mechanical).
Among the sedimentary most diverse - the sands (the most valuable - industrial
river sands).
24. Mineral binders and products based on them.
The most important role in the creation of building structures requiring compounds
detachable in the process of creating a structure.
Classification:
Natural
Artificial.
On the solidification environment:
Air
Hydraulic (both in the liquid layer and air).
Natural: clay, air lime.
Synthetic: adhesives, etc.
The entire construction industry is based on the use of hydraulic air
materials (hydraulic lime).
First place in terms of production - cement (relatively new binder - in
late 19th century). The production industry is based on the production of one
cement brands - Portland cement. Raw materials for cement: clays, sands, limestone.
The modern industry also uses metal ores and waste of various
industries (slags, Woodworking, Paper, Textile Waste
industry). The source product of the preparation of the mixture is a mixture,
consisting of various percentages of various substances and water.
The firing is a high temperature operation, about 1500 degrees.
This is a long process, as a result of which the evaporation of moisture occurs and
transformation and it turns out new Product. After the product is shipped to
"Warehouse" and is there for two weeks. At this stage, physico-
chemical transformations. After natural cooling is carried out
mechanical transformation into a finely dispersive mass.
Ecologically dirty.
Two types of process:
Dry (more eco-friendly, energy savings).
Cement Production Nomenclature:
1) Portland cement (divided by measurements: from 30 to 70)
2) Slagoportland cement
3) special species Cement to create construction structures.
Special cements for defense structures.
TiO 2 is used as in its pure form for decoration, and give color.
Industrial supply - vehicles and railway facilities, sea cement.
Retail packaging (min. From 2 to 50 kg; basic - multi-layered paper from
special Craft Layer). Maximum number of layers - for long
storage. The most progressive - polyethylene bags (reduced conditions
storage and increase storage time).
The main danger is water - an increased content of carbon dioxide (CO 2).
Where the cement is stored in an open form forbidden
vehicles. Special danger in open storage - dustiness
air atmosphere (explosive situation). Absolutely forbidden
using fire.
Aerial binders: magnesian air - gypsum. The main drawback is
exposure to destruction (used only for interior decoration).
Cement-based materials:
Solutions (cement + sand + water)
Dough - for finishing works (cement + sand)
Concretes (cement + shutter + filler)
Reinforcement:
Flat
Volumetric structures (welded structures that are poured liquid
metal). Reinforcement gives strength during deformation.
Nomenclature of reinforced concrete products Great:
Inter-storey overlap
Ladder
Window
Surverent, etc.
Special storage conditions for binders: especially for air lime
and for gypsum. Solid in a moisture-proof room, under the roof, whites
warehouses. Storage time is normalized. When the service life is exceeded
cement increases, because Flowing characteristics fall.
The use of cement solutions has become the main one.
Mineral binding substances, types, properties and application.
MVV are powdered materials capable of mixing them
with water to form plastic dough, which as a result of physical
technical processes gradually hardens in the stone-shaped body. Of them
produce solutions for masonry walls, foundations, furnaces, pipes, concrete,
reinforced concrete, etc. MVV are divided into air (harden and still stored
durability only in air) and hydraulic (solidify and for a long time
keep strength not only in air, but also in water). To airbag
include air lime, gypsum (construction gypsum alabaster, molding
gypsum, anhydritic cement, polymergips, gypsomoto-pozzolanki binders) and
magnesia binders. Hydraulic are more complex in composition (Roman-cement,
portland cement, Slagoportland cement and hydraulic lime, etc.)
Page 19 of 21
Construction products
All buildings consist of the same building elements: the foundation is the base of the building, transmitting the load from the building to the Earth; The frame is the carrying design of vertical racks or columns and horizontal elements based on them. The frame perceives the main loads and transmits them to the foundation, ensuring the strength and stability of the structure as a whole; Organizing design - protects the inner volume of the building from exposure external environment. In order for the building to fulfill its purpose, it is important to choose the key to choose the materials for its design, given the appointment and conditions of its work. Most building materials get processing of wood, stone and brown coal and other organic Materials. Construction materials are divided into non-metals; non-metallic ordeal; cement, materials wall, partition, binders and raw materials for them; Materials of heat and sound insulation; materials finishing polymeric, roofing, waterproofing and sealing; Products asbestos-cement. In a separate class, structures and details of precast concrete products are highlighted. Nermetal construction materials are divided into materials of natural origin (crushed stone and gravel, sand, stingy stones) and artificial (gravel rally, crushed stone and sand porous metallura-gyric slag, clamzit, etc.). Non-metallic building materials include asbestos, mica products, mica products, quartz, kaolin, talc. Cements are a mixture of silicates, aluminates and calcium ferrites, which give them hydraulic ability (solidified in water). Ceramic, stones and blocks of ceramic, stones and blocks of ceramic, stones and blocks include wall, partition and binding materials. natural stoneBlocks made of cellular concrete. Construction ceramic materials and products include clays, ceramic facing products (floor tiles, facade, faders; sewer pipes, drainage and well, mlinic and cement-sand tiles). The heat and sound insulation materials are represented by such materials as: mineral wool, pelite slabs, asbestos-local plates, asbestos-cement-cement plates, plates of foaming, plaster plates sound-absorbing, arbolite plates, plates from basalt fiber, and other finishing poly-measured, roofing, Waterproofing building materials include linoleum different species On a tissue basis and without base, bituminous materials on a cardboard basis (rubberoid), fiberglass materials (glasskerberoid) and other asbestos-cement products include flat and wavy sheets, pipes and clutches asbestos-cement pressure and non-pressure, panels and Plates asbestos cement. The class of structures and parts of precast concrete rooms is divided into subclasses: structures and parts for foundations; construction and details of the framework of buildings and structures; designs, parts of walls and partitions; Plates, panels and flooring and coatings; Designs and details of engineering structures and special purpose; Constructive and architectural and building elements of buildings and facilities. For the construction of walls, partitions, roofs, floors, doors, windows, etc., wood and sawmills are used. Wood in the form of logs of sawn conifers, oak, birch, lime; The logs of plywood and others. Timber includes boards, bars and bars. Metal construction goods include rolled steel of ferrous metals, steel roofing sheet, tin sheet, wire, mesh, fasteners and sanitary equipment and diving. For glazing, glass window, three-layer glass, glass tempered glass, reinforced glass, porridge glass, glass windows. Double glazing, glass blocks, glass tiles, foam glass. Wallpaper, shelves, layered plates are used as finishing materials in construction. Wood-fibrous plates, polyvinyl-chloride film, isople, polyplane, polynesille.
According to the type of raw materials and the method of manufacture Building materials are classified on: natural materials (wood, stone); Materials subjected to only mechanical processing; materials obtained by burning and fighting (ceramics); Mineral-binding substances; Materials obtained by melting (glass, metals); materials obtained in the resulting chemical processing of organic raw materials (synthetic polymers, solvents, bitumen, tar); Materials obtained as a result of technical treatment of organic binders (construction plastics, organic roofing and waterproofing materials).
Types of building materials are classified: by appointment; According to the type of raw materials and the method of manufacture. For appointment, building materials are divided into: structural, which perceive and transmit loads in the buildings system; thermal insulation, whose main task is to minimize the heat transfer process through building structures and ensuring the necessary thermal regime of the room; Acoustic materials used to reduce the level of sound pollution of the room, divided into sound-absorbing and sound insulation; Waterproofing I. roofing materials and used to create waterproof layers on the roofing and other parts of the building of the building exposed to water and moisture; Sealing materials intended for sealing joints in prefabricated structures with tightness for a long service life; decoration Materials, improving the decorative properties of building structures and protect other building materials from the effects of the external environment; refractory, acid-resistant materials; Special materials, etc. A number of materials - cement, lime, concrete, wood - cannot be attributed to any single group of materials, as they are used as raw materials to obtain other materials. For example, concrete is used mainly as a structural material, but some types of concrete (special purpose concrete) are used as a heat insulating material, and concrete based on decorative substitutes is as a finishing material. Raw materials for receiving bitumens, maidens and most synthetic materials are oil and coal . Woods receive lumber. It serves to make wood-chip and wood-fibrous plates. By chemical treatment of wood, film, microcellulose, is obtained.
A significant impact on the properties of the building material is provided by its micro and macro structure. The main structural characteristics of building materials are largely determined by their physical, mechanical, physico-chemical and chemical properties. Physical properties include: average density; porosity; hygroscopic; water reproduction; water, vapor and gas permeability; heat-water, heat and thermal expansion; Fire resistance and refractory; acoustic properties; Frost resistance. Mechanical properties Combine: Flexibility; plastic; thixotropy (the ability to restore its structure after destruction). Physico-chemical properties include: dispersion; hydrophilicity; hydrophobicity; corrosion. The properties of building materials also affect the shape and size of the particles of the solid, from which they consist. Depending on the form, the size of the particles and their structure distinguishes: the grains and the conglomerate structure may have a loose and conglomerate structure. The first consist of separately non-fragrant grains (for example, sand and gravel). Construction materials with the conglomerate structure of grain are firmly interconnected (example - granite); Fibrous and layered materials , in which the fibers are located in parallel to each other, which causes the presence of many properties in these materials in different directions. Such mat-rials are called anisotrops (example - wood). Most building materials have an air pores in size up to 1 cm. The amount, size and characteristic of air pores largely determine the properties of building materials. For example, porous glass is opaque. The various properties of crystalline materials of the same composition may be observed if they crystallize in different forms. For example, graphite and diamond are two crystalline carbon forms. Changing the properties of materials is sometimes achieved by changing the crystal lattice - for example, with thermal processing of metal. Most of the building materials are divided into brands. The brand is a conditional indicator established by the main operational characteristic or by the complex of the main properties of the material. The structural materials of the brand are established by compressive strength (measured in kg / cm 2). Heat insulating materials Marks are assigned to middle density (kg / m). At bitumen - according to a set of basic properties (softening and viscosity temperature). In addition to the main brand there are special stamps that characterize some kind-divided properties of materials.
Group of metal products Includes products that are used in construction and household for various purposes and are made of black and non-ferrous metals. Domestic metal products are divided into: metalwakers of economic use of ferrous metals and their alloys; fasteners; Electrode and firm-alloy industry, tool, sanitary equipment. The fasteners include bolts, nuts, screws, studs, clamps, staples, and construction nails, molding, tall, roofing, tare, finishing and wallpapers.
Tools are divided into the cutting tool (for metal); Mounting, clamping and auxiliary; instrument measuring; Tool Wood cutting machine. IN independent groupnot related to metal household goods, the tool is diamond and from superhard alloys. The cutting tool includes drills from high-speed steel, solid alloys, doped tool shallows of general purpose and for certain materials; carbon steel taps manual, machine-manual and machinery, high-speed taps steel wrath and carbide taps for metric, cylindrical tubular and cylindrical inch thread; Dice threadar round and flat; Senckers from high-speed steel and carbide; Zenkovka, sweep, high-speed steel mills, carbide, from doped and carbon steel; needlopresses; Cutters turning, boring, planing, slim and dentless; Disc saws; broach; fucking and sewers; Rollers are threadcattered; Handicraft canvas and machine.
A fitting and assembly tool includes a control and marking tool (circulating markings, etc.); tool running a blow (hammer, swabs, etc.); Tool cutting manual (engraving cutters, etc.); Instrument gripping and cutting (pliers, passage, ticks); wrenches, pipe, pipes, metal scissors, etc. Screwdrivers seamas-new and special et al.; Auxiliary tool for fastening the cutting tool (coofer, drill, etc.); Tool for the workpieces (vice manual, etc.); sets for the maintenance tool of domestic use, for technical provision of cars, etc.; Tool clamping (sleeve, vice plumbing, etc.); Auxiliary tool (Files are different, Nadfili, etc.). The measuring instrument includes calibers, measures, caliper, micrometers, ruler, etc. Tool Wood cutting machine includes cutters, drills, knives, saws, etc.
Equipment sanitary and technical is divided into means of fixing components to the sled truck and technical equipment (sewer pipes, etc.); Equipment and heating and hot water supply devices (heating boilers, water heaters, etc.); Lock and hardware. A group of lock and hardware includes locks and latches for wooden doors; Pens and loops for wooden windows and doors; Devices shut-off and auxiliary for wooden windows and doors. Cutting locks, overhead, hanging, garage. The locking mechanism of locks can be cylinder, disk, rush and code. Latches can be mortise and overhead.
Domestic metal products also include cabinets and safes; racks and racks; Wall hangers and clothes hangers; Cornices and blinds; Folding stairs, stepladers; Economic shelves, stand and suspension; Metal furniture foldable, etc.
| Table of contents |
|---|
- Classification of construction goods
- Consumer properties
Classification of building materials
1. By origin
b. Artificial
2. In the composition
a. Mineral
b. Organic
c. Combined
3. Output of the feedstock
· Mineral binders;
· Natural stone materials;
· Materials based on mineral binding substances;
· Materials and products from ceramics;
· Materials and products and glasses;
· Materials and wood products;
· Metal-based materials;
· Materials and products based on fibrous substances, paper and polymers.
4. By appointment
· Binding substances;
· Materials for walls and partitions;
· roofing materials;
· Facing and finishing materials;
· Heat and sound insulation materials;
· Floor materials;
· Glazing materials;
· Sanitary equipment.
Characteristics of the range of building goods
I. Mineral binders
For masonry and plaster walls.
1. Air - Keep the strength in the dry environment
· Lime - limestone roasting product. Divide 1 and 2 grades.
· Gypsum (alabaster) is a product of plastering stone processing. Divide 1, 2 and 3 varieties.
· Magnesia binders
2. Hydraulic - retain strength in a wet environment
· Hydraulic lime
1) Portland cement
2) Slagoportland cement
3) special cements
Used in the form construction mixes (Mineral binder, sand and water), concrete (+ crushed stone)
II. Natural stone materials
III. Materials based on mineral binding substances
1. Materials based on plaster
· Plasterboard
· Gypsum decorative decorations
2. Materials based on lime
· Lime-and-sand brick,
· Lime-rally brick,
· Lime-slag brick
3. Cement-based materials
· Lis-you asbestos-cement (slate)
· Asbic cement pipes
· Cement and sand products
§ Wall and foundation blocks,
§ facing
§ Paving tile.
IV. Ceramics-based materials
1. Walls
a. Brick clay 250x120x65 mm
i. Ordinary
iI. Effective
b. Stones 250x120x138 mm
2. Facing and finishing
a. Brick facial
b. Tile facing
c. Mosaic tile
3. Roofing materials
a. Tile
4. Sanitary and hygienic
· Shells,
· Toilet bowls
5. Floor materials
V. Materials and products for glass
|
Subgroup for appointment |
Features, Application |
|
|
Materials for glazing |
Sheet glass |
Ordinary, window |
|
Polished |
Polished, for showcase windows, mirrors |
|
|
Tempered (Stalinitis) |
Increased mechanical strength, thermal resistance, harde the usual sliced \u200b\u200bglass (660-670 ° C). Apply for glazing vehicles, doors, shop windows, for the partition device. |
|
|
Three-layer glass (triplex) |
They are obtained by gluing glass sheets with celluloid, acetylcellulose and other substances. Used in vehicles. The main disadvantage is possible turbidity under the action of light. |
|
|
Glass reinforced |
It has a metal grid thicker, which serves as a frame and increases the strength of stack-la. Release in the form of flat and wavy sheets. The surface can be smooth and patterned. It is used for glazing staircases, veranda, cylinder rooms, partition devices. |
|
|
Patterned glass |
It has a relief pattern on one or both surfaces, so the light dispels well. Semi-chain with rolling between rollers with engraved surface. Release with colorless or color. Apply for glazing partitions in cases where the equal dispersion is required. |
|
|
Double glazed windows. |
For glazing window binding premises. Consist of two steam, hermetically glued together with a period of 15-25 mm. Get from window polished, hardened and patterned glass. It is characterized by low heat transfer, in winter it does not freeze and does not feel. |
|
|
Materials for the device of walls and partitions |
Glass hollow blocks |
Consist of two empty-body halves glued or cooked with each other. On the inner surface of the halves there are ripples of a high-alone about 2 mm, which contribute to the diffusion of light. The air layer inside the block reduces heat and sound conductivity. Sveta blocks of at least 55%. Blocks in shape can be square, rectangular, angular, by nature heat treatment - Annealed and tempered, color - colorless and color. |
|
Profile Glass (Final Production) |
Release in the form of channels (P-shaped strips) and welded box beams. Walls and partitions are lightweight, well mounted, but fragile. |
|
|
Facing and finishing materials. |
Apply for facing and finishing of buildings and rooms for both internal and outer surface - glass tiles of various types. They are beautiful appearance, water resistance and durability. |
|
|
Stemalitis |
The tempered tiles of thickened fox glass covered before handling on one side with color enamels. The heat treatment contributes to both the strengthening of the glass and fixing the paint. |
|
|
Enameled tiles |
We are produced from ordinary glass, covered with a thin layer of color enamel. |
|
|
Tiles marching |
Move from muffled color polished glass. The most common black margins (stained by manganese compounds) |
|
|
Facing tiles Mosaic and carpets |
Motorly with cold pressing of glass powder or pressing the glass mass. These tiles are white, color, with matte and shiny surface, smooth or relief. |
|
|
Heat and sound insulation materials. |
Foamglo |
Fiberglass sheets are obtained by pressing fibers with phenolic, polyester and other SMO-Lami. Fiberglass sheets are produced smooth and wavy. They are used as roofing construction materials, they skip light well, so used for roofing buildings with natural light (attic rooms, trays). Fiberglass sheets are lightweight, pretty durable, corrosion-resistant, have a good appearance, do not require additional per-track and decorative coatings. |
|
Fiberglass |
||
|
Glasswater |
||
|
Glass plastics |
Vi. Wood materials and products
1. Round timber
a. By breeds
· Coniferous
· Least
b. By destination
· For construction (sawmaker)
c. Thick
· From 3 to 7 cm Herse
· From 8 - 11 cm Side
· Over 12 cm log
2. Timber
a. Plates
b. Quarter
c. Boards - sawn timber up to 100 mm thick and the width of dual thickness
d. Bruks - thickness up to 100 mm, width does not exceed double thickness
e. Brux - large sawn timber, width and thickness from 100 to 250 mm
· Two-sided - sculpted on both sides
· Four-sided - sculpted from four sides
f. Gorny - cut during sawing a narrow part of the log, usually with the bark
4. Semi-finished products and finished products
a. Plywood - layered wood materialglued from three or more layers of lush veneer sheets
b. Decorative plywood - lined with decorative coatings
c. Carpentry plates - shields from plated rails on two sides veneer
d. Chipboard - chipboard
e. Fiberboard - Warfather Plate
f. Running products: rings, plinths, platbands, threshing
g. Door and window bindings
h. Shield national teams
VII. Metal-based materials
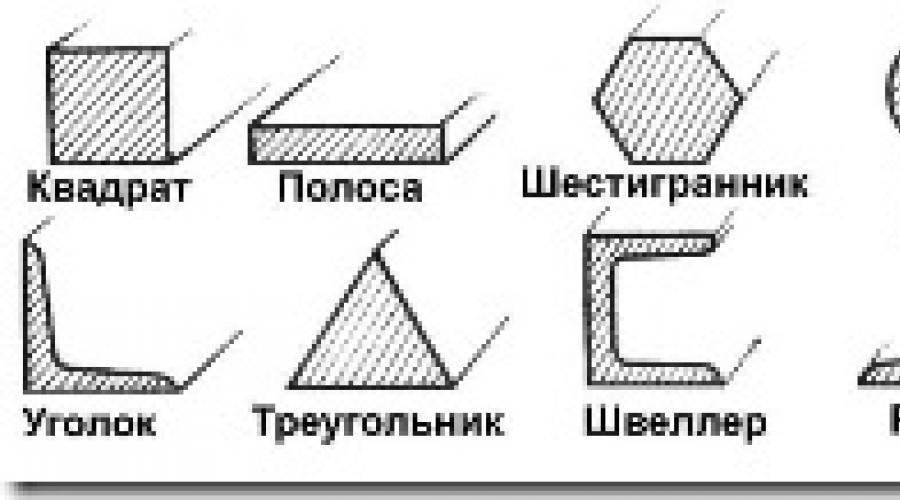
1. Profile (structural)

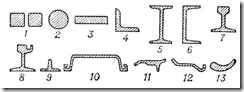
Some profiles of varietal rental: 1 - kidnut; 2 - round; 3 - rectangular (strip); 4 - angular; 5 - 2-way; 6 - challer; 7 - Railway rail; 8 - tram rail; 9 - Tavra; 10 - tongue; 11 - a strip for tractor tracks; 12 - band for rims of trucks; 13 - strip for turbine blades.
2. Roofing materials
a. Black roofing steel
b. Cink Steel
c. Steel tile
d. Profile sheets
e. Aluminum tile
3. Fasteners - used for the production of low carbon and alloyed steel, duralumin and copper alloys (brass, bronze)
a. Wire
b. Wire mesh
f. Rivets
4. Sanitary and hygienic equipment
a. For kitchens - enameled, cast iron and stainless steel
b. Bathrooms - Bath and Pallets Shower
c. For toilet rooms - Tacka wash
d. For furnaces - valves, grate, doors, grids, stoves
e. For the device and repair of systems - pipes, couplings, squares, tees, crosses, nozzles
VIII. Materials and products based on fibrous substances, paper and polymers
1. Based on paper
a) by surface nature
· Smooth
· Close
· Metallized
· Masha
b. Linker
2. Based on polymers
a. For floors
a) Linoleum
1) turning the coverage
· Alkyd
c) Vorsalin
b. Finishing and facing materials
a) Rolled
b) leafy
· Layered plastics
· Siding
c) Tile
3. Based on fibrous
a. Ruberoid - Cardboard with impregnation bitumens
b. Tol - Cardboard with impregnation of tar
c. Pergamine
What depends on the frost resistance of building materials?
What is the indicator judged by thermal conductivity?
What materials refer to non-aging?
What loads are building materials?
For what materials is particularly important is the resistance to the effects of aggressive environments?
Factors affecting consumer properties?