Specific heat capacity table. Density and specific brick heat
Not specific, but a common thermal capacity, in the generally accepted physical sense, is called the ability of the substance to heat. At least such a tutorial on thermal physics - this is a classic determination of heat capacity. (Proper wording). In fact, this is an interesting physical feature. Little familiar to us on the life of the "Side of the Medal". It turns out that when heaving heat from outside (heating, warming up), not all substances react equally to heat (thermal energy) and heated in different ways. Ability Quartz Natural Sand receive, take, hold and accumulate (accumulate) thermal energy called the heat capacity of the sand river. And herself is the physical characteristic of rock, describing the thermophysical properties of the construction sand mixture. At the same time, in different applied aspects, depending on the particular practical case, something one may be important for us. For example: the ability of the substance to take heat or ability to accumulate thermal energy or "talent" to hold it. However, despite some difference, in the physical sense, the properties we need will be described heat capacity of sand material.
A small, but very "ugly snag" with a fundamental nature is that the ability to heat up - thermal container of fine grain breeddirectly connected not only with a chemical composition, a molecular structure of matter, but also with its amount (weight, mass, volume). Because of such "unpleasant" communication, total heat capacity of sand material It becomes too uncomfortable physical characteristic of the substance. Since, one measured parameter, simultaneously describes "two different things". Namely: really characterizes thermophysical properties of sandHowever, "Along the way" takes into account its number. Forming a peculiar integral characteristic in which the "high" thermal physics and a "banal" amount of the substance (in our case is automatically connected: the construction of a bulk material).
Well, why do we need such thermophysical characteristics of bulk material, which is clearly traced "inadequate psyche"? From the point of view of physics, total the heat capacity of the sand breed (the clumsy way) is trying not only to describe the amount of thermal energy capable of accumulating in fine-grained construction material, but also "in terms of telling us" about quantity quartz sand. It turns out absurd, and not intelligible, understandable, stable, correct the thermophysical characteristics of the sand rock. Instead of a useful constant, suitable for practical thermophysical calculations, we "apply" a floating parameter, which is the amount (integral) of the amount of heat taken Sand and its mass or volume of fine-grained rock.
Thanks, of course, for such "enthusiasm", but the number Sand of river wam I can measure it yourself. Having obtained results in a much more comfortable, "human" form. number Sand quartz dry I would like to "extract" mathematical methods and calculations on the complex formula of the general heat capacity of sand material for construction work , at various temperatures, and learn weight (mass) in grams (gr, d), kilograms (kg), tons (TN), cubes (cubic meters, cubic meters, m3), liters (L) or milliliters (ml). Moreover, smart people For a long time, measuring instruments are quite suitable for these purposes. For example: scales or other appliances.
Especially "annoying the floating character" of the parameter: General sand heat capacity. Its unstable, changeable "mood". When changing the "size of a portion or dose", sand heat capacity at different temperatures Immediately changes. More Mine rock, physical value, absolute value heat capacity of sand material - increases. Less amount of rock, value heat mixture thermal capacity decreases. "The disgrace" is somehow it turns out! In other words, the fact that we "have" or how can it be considered a constant describing thermophysical sand characteristics at different temperatures. And it is desirable for us to "have" a clear, permanent coefficient, a reference parameter characterizing thermal properties Quartz sandy mixture, without "references" on the amount of bulk building material (weight, mass, volume). What to do?
Here we for the rescue comes very simple, but "very scientific" method. It comes down to not only to the bail "UD. - Specific", in front of the physical size, but to an elegant solution involving an exception to consideration of the amount of substance. Naturally, "uncomfortable, extra" parameters: mass or volume Sand quartz It is not possible to exclude completely. At least for the reason that if there is no amount of wicked sandy mixture, it will not remain the "subject of discussion" itself. And the substance must be. Therefore, we choose some conditional standard mass of the bulk breed or the volume of sand material, which can be considered a unit suitable for determining the value of the "C" coefficient we need. For sand weight quartz washedSuch a unit of mass of a sandy mixture, convenient in practical application, was 1 kilogram (kg).
Now we heat one kilogram of sand per 1 degree, and the amount of heat (thermal energy)we need to heat the bulk sandy material for one degree - this is our correct physical parameter, coefficient "C", good, quite fully and clearly describing one of thermophysical properties of sand at different temperatures. Note that now we are dealing with the characteristic describing physical property Substances, but not trying to "additionally put us in fame" about its quantity. Conveniently? No words. Quite another matter. By the way, now we are not talking about the overall heat capacity of sand mix. Everything has changed. This is the specific heat capacity of the river sand.which is sometimes called differently. How? Just mass The heat capacity of the Sand Quartz. Specific (UD.) And mass (m.) - In this case: synonyms, they mean here we need here coefficient "C".
Table 1. Coefficient: Specificness of sand (UD.). Mass heat tank river sand. Reference data for bulk building materials natural origin: Mountain breed, sandy mixture.
Sand is considered the most common material.which is used in all spheres of human vital activity especially in construction. It is unlikely that there is modern buildingwherever sand applied, as a component of the material. It is used for concrete mix Or a conventional solution for masonry brick wall.
Dignity
Sand has a number of advantages Thanks to which the building is exploited for many years. To the main one can be attributed:
- seismic resistance;
- well tolerates harsh temperature differences, from severe frost to hot climate;
- low compression The material helps to place a heavy base on it, and at the same time further absorted the whole building. This is particularly relevant in areas with frequent earthquakes;
- water permeability, which allows for cleaning many liquids;
- a wide range of applications in other areas.
For the convenience of determining the heat capacity of the material, in this case, sand, ready-made tables are used, in which calculations are given. They are used by builders for computing.
Thermal conductivity is also an important value, taken into account when planning thermal insulation works. Selection right material It is very important, it depends on it, which amount of thermal energy you have to spend on the heating of the finished room.
The main problem is the low heat capacity of the sand material and the finished room, especially if it is a residential building, requires additional thermal insulation. The thermal conductivity depends on the density of the material itself. Another one an important point It is the humidity of the sand.
As indicated in the table below, the thermal conductivity of sand material increases with its increase.
Table expression of the main parameters of heat thermal conductivity
This table will help both novice builders and those who are not new to this case, quickly and accurately calculate required amount Sand material for future buildings.
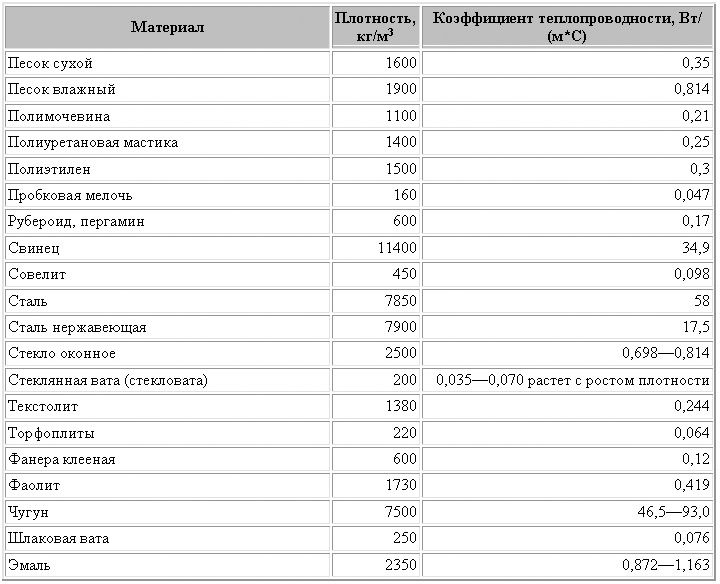
If the construction type of the standard GOST sample is used, then with a mass of 1600 kgm3, the thermal conductivity will be 0.35 W M * hail., And the heat capacity of 840 JKG * hail.
If wet river sand is used, then the parameters will be such: the mass of 1900 kgm3 has a thermal conductivity of 0.814 W M * hail, and the heat capacity 2090 JKG * degree.
All of these data are taken from various manuals on physical quantities and heat engineering tables, which shows many indicators for building materials. So it will be useful to have such a little book.
What sand is best used for making concrete?
The widespread use of sand in construction work allows you to expand the range of applications. It it is a versatile agent for cooking of various types Solution:
- for concrete mixes;
- on the ;
- walls;
- laying walls blocks or brick;
- filling carrier plays;
- production of monolith.
You can still list, the main thing is to understand the essence. But when the various kinds of structures are built with sand with various composition and properties.
A unique property, transition from loose state into a dense. Allows you to use this material for protective and natural depreciation of the structure of the structure.
If you select the production component of concrete, then here construction organizations Yes, and private builders prefer precisely river sand. Its properties allow you to start using without additional manipulations like flushing, such as career.
The cleanest among the mined sands is the one that is mined from the bottom of the current rivers. It passes additional flushing processing and can immediately be used for its intended purpose. The homogeneous mass and the lack of superfluous impurities make this type of sand in demand, despite the cost.
Special material and requires an accurate calculation of the proportions of the components, and its quality depends on the presence of clay rocks in the sand. After all, the properties of clay in improving the graves of the mined material, which directly affects the high-quality grip of sand with other components of the concrete mixture, including cement.
According to the characteristics sand is still divided into classes:
- first grade;
- second class;
- special sands.
Each of the listed groups is used to use concrete products, but only for a narrow circle. For example, the first class is used to cast concrete, whose main characteristics are:
- quality;
- high resistance to external influences;
- a sharp drops of temperature, including frost resistance.
Sands belonging to the second class are used only for the manufacture of materials that do not require increased moisture resistance, for example, for tiles or facing structures.
Special sand mixes necessary when erecting concrete or reinforced concrete structures. Such mixtures make it possible to strengthen a number of indicators for compression and resistance to precipitates of atmospheric environments.
For more information about the properties and application of sand, see the video:
Conclusion
Sand is a unique natural materialwhich helps to solve many building issues. The properties of this material allow it to use it when erecting the most complex structures.
And due to the low heat capacity, this material is ideal for the construction of the premises where low temperatures are required without sudden drops.
Items for centuries of sand was used by a person, and was considered the most reliable building material that nature created. The diversity of species and fields of application helps to think in advance what properties will have a built building.
The ability of the material to hold heat is rated its specific heat . The amount of heat (in KJ), which is necessary to increase the temperature of one kilogram of the material for one degree. For example, water has a specific heat capacity equal to 4.19 kJ / (kg * k). This means, for example, that to increase the temperature of 1 kg of water at 1 ° K, 4.19 kJ is required.
| Material | Raft- kg / m 3 |
Heat- Capacity, KJ / (kg * k) |
Coefficient Cenage heat the wire- VT / (m * k) |
Mass there for heat battery rings 1 gd heat at δ \u003d 20 k, kg |
Relation feather naya mass there Success to mass of water, kg / kg |
Volume there for heat battery Ringing 1 GJE heat at δ \u003d 20 k, m 3 |
Relation feather volume there Water volume, m 3 / m 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granite, Galka | 1600 | 0,84 | 0,45 | 59500 | 5 | 49,6 | 4,2 |
| Water | 1000 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 11900 | 1 | 11,9 | 1 |
| Glauberova Salt (sodium sulfate decahydrate) | 14600 1300 |
1,92 3,26 |
1,85 1,714 |
3300 | 0,28 | 2,26 | 0,19 |
| Paraffin | 786 | 2,89 | 0,498 | 3750 | 0,32 | 4,77 | 0,4 |
For water heating plants and liquid heating systems, water is best used as a heat accumulating material, and for air heliums - pebbles, gravel, etc. It should be borne in mind that the pebble heatacumulator with the same energy intensity compared to the water heatacumulator has 3 times a larger volume and takes 1.6 times large area. For example, a water heat acceumator with a diameter of 1.5 m and a height of 1.4 m has a volume of 4.3 m 3, while a pebble heataccumulator in the form of a cube with a side of 2.4 m has a volume of 13.8 m 3.
The recycling density of heat is largely depends on the accumulation method and the kind of heat accumulating material. It can be accumulated in a chemically associated form in fuel. At the same time, the accumulation density corresponds to the heat of the combustion, kW * h / kg:
- oil - 11.3;
- coal (conditional fuel) - 8.1;
- hydrogen - 33.6;
- wood - 4.2.
With thermochemical accumulation of heat in the zeolite (adsorption processes - desorption), 286 W can accumulate 26 W * h / kg of heat when the temperature difference is 55 ° C. The recycling of heat in solid materials (rock rock, pebble, granite, concrete, brick) with a temperature difference of 60 ° C is 14 ... 17 W * h / kg, and in water - 70 W * h / kg. With phase transitions of the substance (melting - hardening) accumulation density is significantly higher, W * h / kg:
- ice (melting) - 93;
- paraffin - 47;
- hydrates of inorganic acid salts - 40 ... 130.
Unfortunately, the best building materials contained in Table 2 - concrete, the specific heat capacity of which is 1.1 kJ / (kg * k), holds only the ¼ of the amount of heat that stores the water of the same weight. However, the density of concrete (kg / m 3) significantly exceeds the density of water. In the second column of Table 2 shows the densities of these materials. Multiplying the specific heat capacity on the density of the material, we obtain the heat capacity on cubic meter. These values \u200b\u200bare given in the third column of Table 2. It should be noted that water, despite the fact that it has the smallest density of all the above materials, has a heat capacity of 1 m 3 above (2328,8 kJ / m 3) than the remaining table materials, By virtue of its significantly greater specific heat capacity. The low specific heat capacity of concrete is largely compensated by its large mass, due to which it holds a significant amount of heat (1415.9 kJ / m 3).
It is believed that any sand is suitable for construction work. But it is not. First, it is necessary to apply only special construction types. Secondly, it is necessary to take into account their individual characteristics.
The proportion and heat capacity of this material play an important role when choosing one of its species, and will be told in this article.
His specific characteristics depend on the type of material. There are several types of its varieties. By origin is divided into natural and artificial. The first form, depending on the place of production, has the following varieties:
Career
Career Sand is mined as a result of destruction mountain breeds. Its grains can be from 0.16 to 3.2 mm. Because of the peculiarities of production, low quality is obtained, as it contains many impurities in the form of clay and dust.
Crushed
It turns out due to the destruction and grinding of rocks. This process occurs on special equipment, so mining of this sand is reflected at its high cost. Due to the resulting incorrect form The sands are well associated with each other and other construction substances. When adding such a material, the consumption of concrete is reduced. 
Application: It is used for concrete structures, when pouring roads and paths, as well as as a filler for dry mixtures.
The above-mentioned sand varieties are distinguished by color. So, the career has a yellow and brown shade, and the river occurs cream and gray.
Artificial
It is considered as such, because there is a special processing, after which the material is obtained, differing in properties from its original. Created by crushing natural stones. 
Quartz
It is the most demanded of all artificial species. It is obtained as a result of grinding white quartz. After some processing, a homogeneous composition is made without impurities. This feature makes it possible to calculate the exact dimensions of the future design. 
Application: Quartz species is widely used in finishing and decorative work, sometimes add it when creating cement mortarBut this is extremely rare. It is usually included in the paint, putty and drain filters.
There is also molding sand, it is used during molding in metal models.
Definition of value
This value is equal to the mass placed in a unit of volume. Simply put - density. Most often in the reference literature is measured in g / cm 3 or kg / m 3.
The specific weight of the sand depends on the amounts contained in it impurities and the deafness of the material. The large content of water increases the proportion per unit volume. Also, this figure will depend on the place of storage of sand, which happens:
- natural occurring;
- the location of the material by the mound;
- artificial seal.
The same type of sand under these conditions will have different meanings.
According to GOST 8736-77 it is indicated that the proportion construction sand May fluctuate from 1150 to 1700 kg / m 3.
The table for example shows several values \u200b\u200bof its separate varieties.
| Sand view | Specific weight in kg / 1 m 3 |
| River-altogether | 1200-1700 |
| 1650 | |
| 1590 | |
| Career | 1500 |
| Nautical | 1620 |
| Quartz | 1600-1700 |
| Wet | 1920 |
Heat capacity
This is the ability of the material to take, accumulate and hold energy. The heat capacity is an indicator of the thermophysical properties of the sand. The ability to heat up depends on chemical composition, structures and quantities of the material used. therefore general It will depend on its dryness. It is important for cement compositions and concreting walls.
| Sand variety | Specific heat in KJ / kg per 1 0 |
| Wet quartz | 2,09 |
| River Dry | 0,8 |
| Career | 0,84 |
| Nautical | 0,88 |
The construction of the sand is a universal material, without any construction. This is an environmentally friendly component of solutions and mixtures. Sustainable burning and not subject to rotting. When choosing its type with a high specific thermal conductivity, a concrete structure with it will accumulate heat and an optimal microclimate will be created indoors. This condition can persist quite a long time. Using the sand with a high indicator swelling It will help to save on cement.